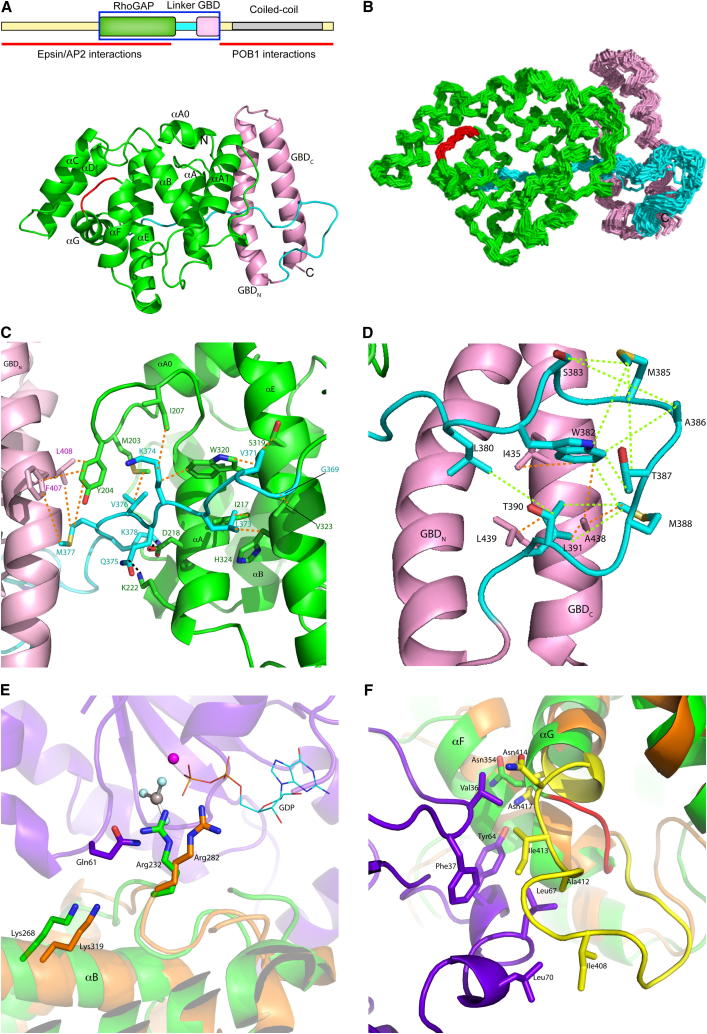
Figure 1.
Structure of the RLIP76 GAP-GBD Didomain
(A) The schematic domain structure of RLIP76 is shown above the closest structure to the mean. The limits of the construct whose structure is shown are outlined in blue. In this and all subsequent figures, the RhoGAP domain is colored green, the linker between the domains is cyan, and the GBD is pink. The loop between helices αF and αG is colored red.
(B) The 35 lowest-energy structures calculated of the RLIP76 didomain.
(C) Summary of the assigned distance restraints between the N-terminal half of the linker and the RhoGAP-GBD. Distance restraints were observed between the atoms connected by orange dashed lines. For clarity, only a single restraint for each residue pair is shown. Contacts between Asp218 and Lys222 in helix αA and the linker are shown as black dashed lines.
(D) Summary of the assigned distance restraints between the hairpin of the linker and GBD and within the linker hairpin. Distance restraints were observed between the linker and the GBD for the atoms connected by orange dashed lines. The hairpin in the linker is defined by a number of distance restraints between atoms, shown as green dashed lines. For clarity, only a single restraint for each pair of residues is shown.
(E) Comparison of the p50 RhoGAP-Cdc42 complex and the RLIP76 GAP domain. Cdc42 is purple, RLIP76 GAP is green, and p50 RhoGAP is orange. GDP is shown in a wire-frame representation, the Mg2+ ion is pink, and BeF3 is shown in a ball-and-stick representation. The arginine finger at the active site and the secondary lysine are oriented correctly in the RLIP76 GAP domain to aid catalysis. The positions of Arg232RLIP76 and Arg282p50 are the same, and the side chains are oriented in the same direction in both RLIP76 and the p50 RhoGAP-Cdc42 transition-state complex (PDB ID code 1GRN). Similarly, Lys268RLIP76 is oriented so that it can support the position of the arginine finger loop in a similar manner to Lys319p50.
(F) The loop between helices αF and αG is truncated in the RLIP76 GAP domain. The RLIP76 GAP domain (in green) has a shorter loop (shown in red) between the two helices. In the complex formed between Cdc42·GMPPNP (purple) and p50 RhoGAP (orange), several contacts are made by the longer loop (shown in yellow). The only contact that remains is at the beginning of the αG helix, where Asn414 in p50 RhoGAP makes a hydrogen bond with Tyr64. The equivalent residue in RLIP76 is Asn354, but this is not sufficient for a high-affinity interaction. The residues involved in interactions between Cdc42 and p50 RhoGAP are shown in a stick representation.