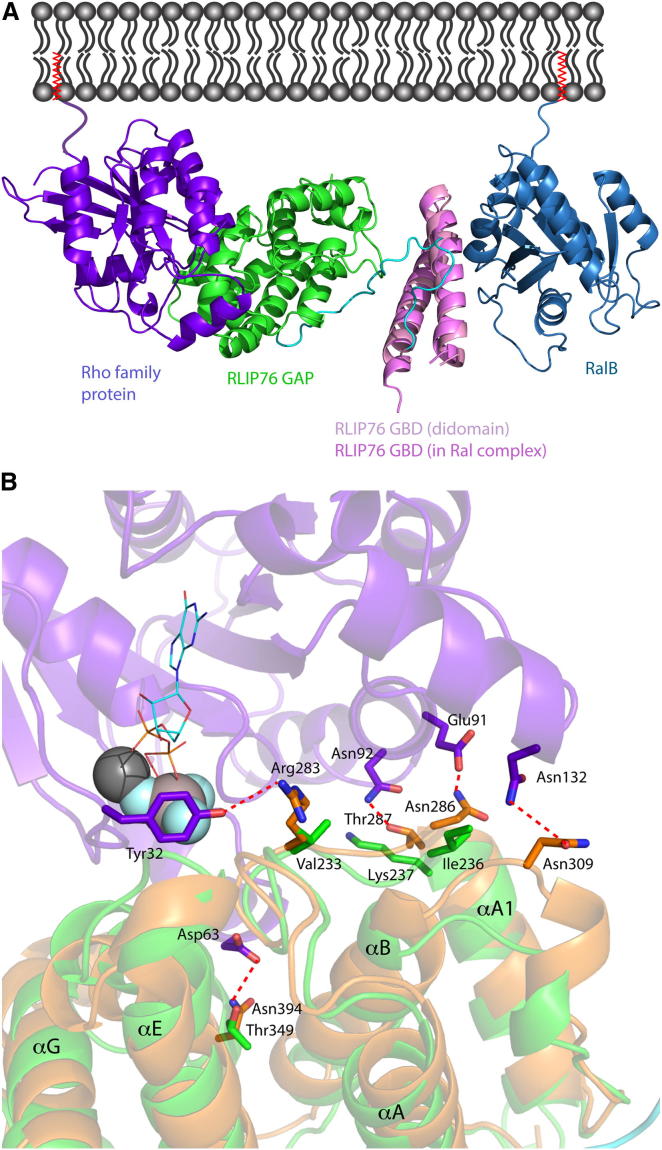
Figure 5.
RLIP76 GAP-GBD Interactions with Ral and Rho Small G Proteins
(A) The RLIP76 GAP-GBD didomain can simultaneously interact with Ral and Rho family proteins. The model of the Cdc42·GMPPNP-didomain complex was superimposed over the RLIP76 GBD onto the RLIP76-RalB complex structure. Cdc42 is purple-blue, the RLIP76 GAP domain is green, the linker between the GAP and GBD is cyan, the GBD is in two shades of pink, and RalB is sky blue. The binding of Cdc42 and RalB together is possible because the binding sites are on the exterior faces of the two domains that make up the didomain. The orientation of the two G proteins is such that their C-terminal helices are pointing toward one side of the trimer and their C-terminal isoprenyl groups (red) will be able to simultaneously engage the lipid bilayer (gray).
(B) Interactions in the Cdc42·GDP·AlF3-p50 RhoGAP transition-state complex that would not be conserved in the equivalent complex with RLIP76. The secondary structures of Cdc42 (purple), RLIP76 GAP (green), and p50 RhoGAP (orange) are semitransparent for clarity. The GDP is shown in a wire-frame representation, Mg2+ is a dark gray sphere, and AlF3 is a light gray sphere surrounded by three pale blue spheres. Side chains of Cdc42 and p50 RhoGAP involved in interactions are shown in a stick representation and colored in the same scheme as the secondary structures. The equivalent residues in RLIP76 GAP are also shown as sticks.