Figure 1.
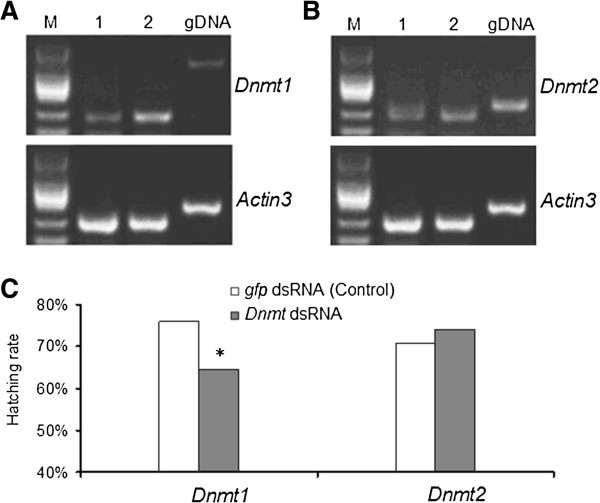
Summary of RNAi depletion experiments. (A), (B) Semi-quantitive RT-PCR validation of the effects of RNAi knockdown on the Dnmt1(A) and Dnmt2(B), indicating obvious decrease of expression level of Dnmt1(A) and Dnmt2(B). Lane 1 indicate amplification using cDNA from Dnmt1 RNAi eggs (A) and Dnmt2 RNAi eggs (B), respectively; Lane 2 indicate amplification using cDNA from Non-specific RNAi control (by embryonic microinjection of gfp dsRNA) eggs. gDNA, PCR using genomic DNA as template to control DNA contamination; M, DNA marker DL2000 (TakaRa, Japan). Actin3 is used as the internal control for Semi-quantitive RT-PCR. (C) Hatching rate of the treated eggs with Dnmt1 RNAi and Dnmt2 RNAi, indicating that RNAi knockdown of Dnmt1 significantly reduces hatched eggs compared to control, but not for Dnmt2. * significant differences as determined by chi-squared test (p < 0.01).
