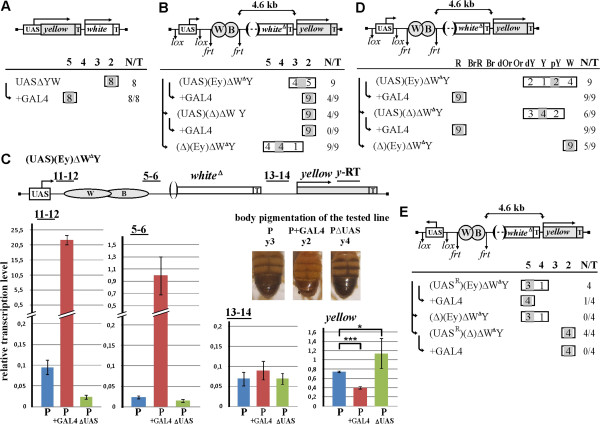
Figure 3.
Transcription through the yellow enhancers leads to their inactivation. (A) UAS∆YW transgenic lines. The UAS promoter drives expression of the yellow gene. The downstream white gene was used as a marker to select transgenes. The color scale for yellow (grades 5 to 2) is indicated above the horizontal line. Grade 5 corresponds to wild-type pigmentation; grades 4 and 3 correspond to partial stimulation of the yellow gene by enhancers; grade 2, to the basal level of yellow expression in the absence of enhancers. Grade 1, corresponding to complete loss of yellow expression, is not shown, because no lines with such a phenotype were obtained in this study. (B) (UAS)(Ey)∆W∆Y; the UAS promoter drives transcription through the yellow enhancers. The white gene with deleted promoter was used as a spacer. (C) Quantification of (UAS)(Ey)∆W∆Y transcripts by RT-PCR. Positions of primer pairs (11-12, 5-6, 13-14) are indicated. RT-qPCR was conducted on mRNAs isolated from transgenic lines at the mid-late pupae stage. Error bars indicate standard deviations. *P< 0.05; ***P< 0.005. For other designations, see Figure 1. (D) Summarized results of eye phenotype analysis in (UAS)(Ey)∆W∆Y transgenic lines. (E) (UASR)(Ey)∆W∆Y; the UAS promoter drives transcription in the direction from the enhancers.