Abstract
Background
Haemonchus contortus (order Strongylida) is a common parasitic nematode infecting small ruminants and causing significant economic losses worldwide. Knowledge of genetic variation within and among H. contortus populations can provide a foundation for understanding transmission patterns, the spread of drug resistance alleles and might assist in the control of haemonchosis.
Methods
152 H. contortus individual adult worms were collected from seven different geographical regions in China. The second internal transcribed spacer (ITS-2) of the nuclear ribosomal DNA and mitochondrial nicotinamide dehydrogenase subunit 4 gene (nad4) were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and sequenced directly. The sequence variations and population genetic diversities were determined.
Results
Nucleotide sequence analyses revealed 18 genotypes (ITS-2) and 142 haplotypes (nad4) among the 152 worms, with nucleotide diversities of 2.6% and 0.027, respectively, consistent with previous reports from other countries, including Australia, Brazil, Germany, Italy, Malaysia, Sweden, the USA and Yemen. Population genetic analyses revealed that 92.4% of nucleotide variation was partitioned within populations; there was no genetic differentiation but a high gene flow among Chinese populations; some degree of genetic differentiation was inferred between some specimens from China and those from other countries.
Conclusions
This is the first study of genetic variation within H. contortus in China. The results revealed high within-population variations, low genetic differentiation and high gene flow among different populations of H. contortus in China. The present results could have implications for studying the epidemiology and ecology of H. contortus in China.
Keywords: Haemonchus contortus, Genetic variation, ITS-2, nad4, China
Background
Haemonchus contortus is a trichostrongyloid nematode and one of the major pathogens affecting small ruminants worldwide [1]. The adult female of this species produces large numbers of eggs, which are excreted in hosts’ faeces. The eggs hatch on pasture and continue to develop under moist conditions to third-stage larvae (L3s). L3s are then ingested by a suitable host animal and eventually establish as dioecious, adult worms [2]. The blood-feeding activity of adults causes anaemia, oedema, diarrhoea and even death [3], consequently causing serious production and economic losses, particularly in tropical and temperate regions of the world [4].
Population genetic studies of H. contortus in the USA have shown that this species exhibits high within population variation and low genetic differentiation within continuous geographical regions, likely ascribing to high gene flow influenced by host movement [5,6]. However, strong barriers to gene flow have been observed on a global scale, which appear to be attributed to poor dispersal ability of the parasite and restricted opportunities for host movement across continents [7]. Other research, focused on domestic and wild animals, has found high genetic variation and relatively low host specificity for H. contortus within Brazil and Italy [8,9].
Population genetic studies of H. contortus have been conducted in a wide range of geographical regions of the world, including Australia, Brazil, Europe, Malaysia, and the USA [5,7-12]. However, surprisingly, nothing is known about genetic variability within H. contortus in China, in spite of its endemic status and economic impact in this country [13,14]. Therefore, in the present study, we explored genetic variation within and among seven populations of H. contortus from southwest, central and northeastern regions of China, employing the second internal transcribed spacer (ITS-2) of nuclear ribosomal DNA and the mitochondrial nicotinamide dehydrogenase subunit 4 (nad4) gene as markers.
Methods
Parasite material
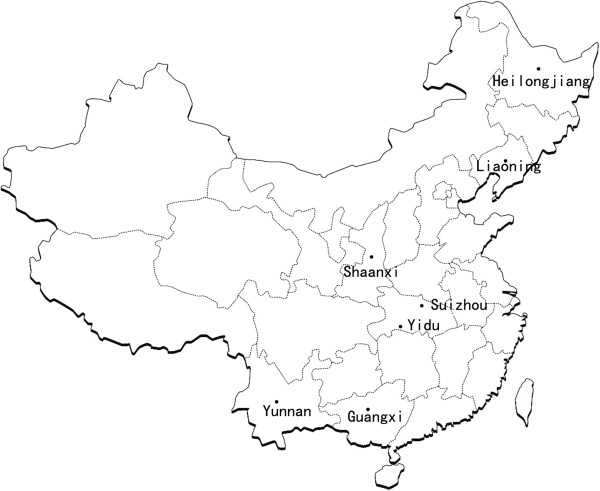
In total, 152 individual adult specimens of H. contortus were collected from the abomasa of slaughtered sheep or goats from seven geographical locations in tropical to subtropical climate zones and six provinces of China (Figure 1 and Table 1). Geographical locations were separated by distances of 370 to 4000 km. Samples from Liaoning and Heilongjiang were from sheep, whereas those from other regions were from goats. The adult specimens of H. contortus (17 to 24 per population) were washed extensively in physiological saline, stored in 70% ethanol and then sent to the College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan. Upon arrival, individual worms were identified morphologically, according to Lichtenfels et al. (1994) [15].
Figure 1.
Sampling sites. Seven different geographical locations in China (longitudes and latitudes given in Table 1) at which adult Haemonchus contortus were collected from sheep or goats.
Table 1.
Sources of 152 adults of Haemonchus contortus representing seven different geographical locations in China, and the numbers of ITS-2 genotypes and nad 4 haplotypes
| Localities (longitude, latitude) | No. of ITS-2 amplicons sequenced | No. of ITS-2 genotypes | No. ofnad4 amplicons sequenced | No. ofnad4 haplotypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suizhou |
22 |
8 |
22 |
21 |
| (112°43′E,31°19′N) | ||||
| Yidu |
17 |
6 |
17 |
16 |
| (111°47′E,30°39′N) | ||||
| Guangxi |
23 |
5 |
23 |
23 |
| (108°3′E,22°8′N) | ||||
| Yunnan |
22 |
8 |
22 |
21 |
| (102°42′E,25°04′N) | ||||
| Shaanxi |
23 |
6 |
23 |
23 |
| (107°40′E,33°39′N) | ||||
| Liaoning |
24 |
8 |
24 |
23 |
| (123°38′E,41°08′N) | ||||
| Heilongjiang |
21 |
6 |
21 |
20 |
| (124°19′E,45°46′N) | ||||
| Totals | 152 | 18 | 152 | 142 |
Isolation of genomic DNA
Total genomic DNA was isolated from individual worms using sodium dodecyl-sulfate/proteinase K treatment [16], followed by spin-column purification (Wizard™ DNA Clean-Up, Promega). DNA samples were stored at -20°C until use.
PCR amplification and sequencing
ITS-2 (~350 bp) was amplified using the conserved primers: NC1 (5′-ACGTCTGGTTCAGGGTTGTT-3′) and NC2 (5′-TTAGTTTCTTTTCCTCCGCT-3′) [17]. A region (800 bp) of the nad4 gene was amplified by PCR using primer1-F (5′-GGATTTGGTCAGCAAATTGAA-3′) and primer2-R (5′-GCCTGCAAATGAATTAACA-3′) [7]. PCR (25 or 50 μl) was performed in 10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.3, 50 mM KCl, 4 mM MgCl2, 250 μM each of dNTP, 100 pmol of each primer and 1 U Taq polymerase (TaKaRa) under the following conditions: initial denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, followed by 30 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 55°C for 30 s and extension at 72°C for 1 min, with a final extension of 72°C for 5 min.
All PCR products were examined on agarose gels (1.5%) to verify that they represented single bands, column-purified (Wizard PCR-Preps, Promega) and then sequenced directly (BigDye Terminator v.3.1 cycle sequencing kit, Applied Biosystems) in an automated sequencer (PRISM3730, ABI) using appropriate forward and reverse primers (in separate reactions). Forward and reverse sequences were merged, consensus sequences determined and then deposited in the GenBank database.
Data analysis
Sequences were aligned over a consensus length (231 bp for ITS-2 and 412 bp for nad4) using the program Clustal W within MEGA v.5.0 [18]. Pairwise comparisons were made with previously published sequences, and identities (%) calculated using the program BioEdit [19].
The phylogenetic analysis was conducted using the neighbour-joining (NJ), maximum parsimony (MP) and maximum likelihood (ML) methods, respectively, based on the Tamura -Nei model [18]. Confidence limits were assessed using bootstrap procedure with 1000 pseudo-replicates for NJ, MP and ML trees, and other settings were obtained using the default values in MEGA v.5.0 [18]. A 50% cut-off value was implemented for the consensus tree. The Collapse program online (http://sing.ei.uvigo.es/ALTER/) was used to define haplotype sequences. The diversity indices (Fst and Nst) were calculated using the program DnaSP5.1 [20] to evaluate degree of gene flow among populations. Tajima’s D[21] and Fu’s Fs [22] were also calculated to test neutrality using the same program (DnaSP 5.1) [20]. To estimate genetic diversity within and among populations (isolates), the hierarchical analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) was performed using the Arlequin 3.1 package [23]. For this analysis, the data set was divided into three groups. Groups 1, 2 and 3 contained samples from Southwest (Guangxi, Yunnan), Central (Suizhou, Yidu, Shaanxi) and Northeast (Liaoning, Heilongjiang) China, respectively. The median joining (MJ) network [24] was drawn using the program Network v.4.6.1.1 to study of haplotype relationships. In addition, 176 nad4 sequences from previous studies [5,8,10] were retrieved from GenBank and used for comparisons. Information on geographical origins, accession numbers and parasite codes are given in Table 2.
Table 2.
Fst values between Haemonchus contortus populations of China and those from other four countries calculated from the nad 4 sequence data
| Geographical location | GenBank accession no. | No. of sequences | Fst | π |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malaysia |
HQ660255-HQ660308 |
54 |
0.05841 |
0.03545 |
| Italy |
AJ429793-AJ429809 |
17 |
0.14407 |
0.03263 |
| Yemen |
HQ660309-HQ660367 |
59 |
0.26710 |
0.03462 |
| The USA |
AF070736-AF070785 |
46 |
0.41294 |
0.02512 |
| China | KC429944-KC430085 | 142 | - | 0.02745 |
A total of 176 nad4 sequences were retrieved from the GenBank database for comparison. The nucleotide diversity (π) within each population was also calculated.
Results
Sequences analyses
ITS-2 sequences were determined from 152 worms from seven different geographical locations in China (see Table 1). After sequence editing and alignment, a consensus length of 231 bp was obtained for all specimens. The analysis of the 152 ITS-2 sequences revealed 18 distinct genotypes (sequence data are publicly available under accession numbers KC415117-KC415134 for ITS-2), with sequence identities ranging from 97.4% to 100%, when compared with each other or with two reference sequences for H. contortus (GenBank accession nos. X78803 and EU084691; Table 3). These sequences were also compared with two publicly available ITS-2 sequences of H. placei (accession nos. X78812 and AJ577466), revealing the nucleotide identities of 96.1 to 98.2%. The alignment of all 18 ITS-2 sequences with the reference sequence X78803 revealed six substitutions at the nucleotide positions (10, 18, 21, 22, 123 and 196; see Additional file 1). These substitutions represented four transversions (one A < - > C, one G < - > C and two A < - > T substitutions) and two transitions (T < - > C). The nucleotide diversities and genotype diversities among the 18 ITS-2 sequences of H. contortus from China ranged from 0.0054 to 0.0084 and from 0.609 to 0.824, respectively (Table 4).
Table 3.
Pairwise identities (%) among the 18 ITS-2 sequences of Haemonchus contorts representing 152 adults of H. contortus from China using selected sequences for H. contortus and H. placei from the GenBank database
| Sample code | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Hlj10 (KC415117) |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2-Ln9 (KC415118) |
99.5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3-SZ9 (KC415119) |
99.5 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 4-Sz13 (KC415120) |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 5-Yd2 (KC415121) |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 6-Yn16 (KC415122) |
99.1 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 7-Yd14 (KC415123) |
99.5 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 8-SZ18 (KC415124) |
99.5 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 9-Sz22 (KC415125) |
98.7 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 10-Sz21 (KC415126) |
99.1 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
99.1 |
98.2 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 11-Sx7 (KC415127) |
99.1 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 12-YD7 (KC415128) |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 13-Sz1 (KC415129) |
98.2 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
98.2 |
97.8 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 14-Sz12 (KC415130) |
98.2 |
98.7 |
97.8 |
97.8 |
97.4 |
98.2 |
97.8 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 15-Ln1 (KC415131) |
97.8 |
98.2 |
98.2 |
98.2 |
97.8 |
97.8 |
97.4 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 16-Gx3 (KC415132) |
98.7 |
99.1 |
98.2 |
98.2 |
97.8 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 17-Yn20 (KC415133) |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
| 18-Gx7 (KC415134) |
99.1 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
| 19-H.contortus (X78803.1) |
99.1 |
98.7 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
99.1 |
98.2 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
99.1 |
98.2 |
99.1 |
98.2 |
98.2 |
98.7 |
97.8 |
98.7 |
98.2 |
- |
|
|
|
| 20-H.contortus (EU084691.1) |
100 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.5 |
99.5 |
98.7 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
98.2 |
98.2 |
97.8 |
98.7 |
98.7 |
99.1 |
99.1 |
- |
|
|
| 21-H.placei (X78812.1) |
97.8 |
97.4 |
98.2 |
97.4 |
97.8 |
96.9 |
97.4 |
97.4 |
97.4 |
97.8 |
96.9 |
97.8 |
96.9 |
96.9 |
97.4 |
96.5 |
97.4 |
96.9 |
98.7 |
97.8 |
- |
|
| 22-H.placei (AJ577466.1) | 97.4 | 96.9 | 97.8 | 96.9 | 97.4 | 96.5 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 97.4 | 96.5 | 97.4 | 96.5 | 96.5 | 96.9 | 96.1 | 96.9 | 96.5 | 98.2 | 97.4 | 99.5 | - |
Table 4.
Diversity and neutrality indices for different populations of Haemonchus contortus from seven different geographical locations in China, calculated from ITS-2 and nad 4 nucleotide data sets
| |
ITS-2 |
|
nad4 |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Gd | π | Hd | π | D | Fs |
| SZ |
0.649 |
0.0083 |
0.996 |
0.0212 |
-1.3764 |
-12.703 |
| YD |
0.824 |
0.0069 |
0.993 |
0.0205 |
-0.0442 |
-7.669 |
| GX |
0.609 |
0.0054 |
1.000 |
0.0226 |
-1.6408 |
-16.558 |
| YN |
0.654 |
0.0057 |
0.996 |
0.0369 |
-0.6390 |
-8.057 |
| SX |
0.708 |
0.0075 |
1.000 |
0.0178 |
-1.6031 |
-19.345 |
| LN |
0.656 |
0.0084 |
0.996 |
0.0263 |
-1.1294 |
-12.808 |
| HLJ | 0.824 | 0.0058 | 0.995 | 0.0196 | -1.4605 | -12.297 |
Abbreviations: haplotype diversity (Hd), nucleotide diversity (π), Tajima’s D (D), Fu’s Fs (Fs), genotype diversity (Gd). Locations: Suizhou (SZ), Yidu (YD), Guangxi (GX), Yunnan (YN), Shaanxi (SX), Liaoning (LN) and Heilongjiang (HLJ).
From the 152 nad4 amplicons, 142 distinct haplotypes (all with open reading frames) were defined (Table 1; sequence data are publicly available under accession numbers KC429944-KC430085 for nad4). Among 142 unique haplotypes, 73 parsimony informative sites were identified. Nucleotide diversities ranged from 0.0178 to 0.0369, and the haplotype diversity ranged from 0.993 to 1.000 for the seven distinct populations of H. contortus (Table 4). The highest nucleotide diversity estimated was for the H. contortus population from Yunnan. Tajima’s D and Fu’s Fs are also shown in Table 4; their low negative values implied no significant deviation from neutrality.
Phylogenetic analysis
Trees were constructed using the nad4 sequence data for H. contortus from China, using an nad4 sequence of H. placei (accession no. AF070825) as the outgroup. The tree revealed a relatively continuous variation in genetic distance among haplotypes (Additional file 2). There was a random distribution of sequences representing different locations, with weak support (< 50%) for some nodes. There were no obvious boundaries among individuals in the phylogenetic trees, except that some individuals from the Yunnan population grouped with moderate nodal support (72%), with one sequence from Guangxi and one cluster contained one sequence from Yunnan and three sequences from Liaoning with strong nodal support (90%). Consistent with the results obtained for the NJ tree, analysis of the nad4 sequences using MP and ML methods, respectively, produced phylogenetic trees with similar topologies (not shown). Extending the analyses, to discern the relationships among 142 haplotypes, a parsimony network was constructed (Figure 2). The network profile showed that there was no preferential or distinct grouping of specimens according to geographical region, except for several individuals from Yunnan.
Figure 2.
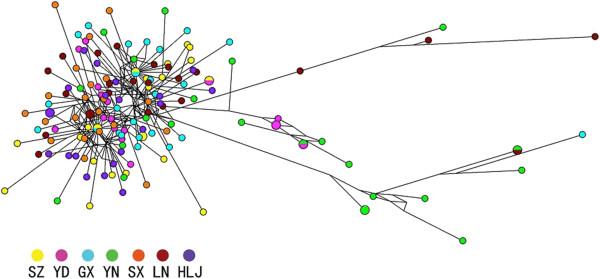
The median joining network of 142 nad4 haplotypes representing 152 individuals of Haemonchus contortus from seven different geographical locations in China. The different coloured dots represent haplotypes from the different populations/locations: SZ: Suizhou; YD: Yidu; GX: Guangxi; YN: Yunnan; SX: Shaanxi; LN: Liaoning; HLJ: Heilongjiang.
In order to genetically compare H. contortus from China with those from other parts of the world, according to the approach used by Troell et al. (2006) [7], ten nad4 sequences, chosen randomly from the Chinese sample set and from each of the four other H. contortus populations representing other countries (Italy, Malaysia, the USA and Yemen) were included (Figure 3). The three methods produced consensus trees, in which there was no clear grouping according to country (at pp > 80%). In contrast, on three occasions, two samples from the same country (two each from China, Malaysia and the USA) grouped together with strong nodal support (pp > 80%). In addition, five samples from Yemen grouped together with low support (50%).
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree constructed using 50 nad4 sequences from Haemonchus contortus from five different countries. The bootstrap values of >50% were displayed in the tree. Forty nad4 sequences of H. contortus were retrieved from the GenBank database and used for comparison; ten sequences represented each country: the USA (accession nos. AF070736-AF070745 [5]); Italy (AJ429793-AJ429802 [8]); Malaysia and Yemen (HQ660353-HQ660362 and HQ660269-HQ660278 [9]). Haemonchus placei (accession no. AF070785) was used as the outgroup. Abbreviations: Ch: China; It: Italy; Ma: Malaysia; USA: United States of America; Ye: Yemen.
Population genetic structure
The random distribution of 142 nad4 haplotypes from Chinese samples across the parsimony network (Figure 2) did not support any particular genetic structure among H. contortus specimens, which is corroborated by the low pairwise Fst/Nst values (Table 5), despite that they originated from different geographical locations. Although Fst and Nst were usually low between populations, ranging from -0.00005 to 0.19774 for Fst and -0.00332 to 0.20091 for Nst, the Yunnan population showed the highest level of genetic differentiation from other populations in China, with Fst values ranging from 0.08288 to 0.19774 and Nst values from 0.08386 to 0.20091 (Table 5).
Table 5.
Pairwise Fst and Nst values between Haemonchus contortus populations from seven different geographical locations in China, calculated from the sequences of the nad 4 haplotypes
| Location | SZ | YD | GX | YN | SX | LN | HLJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZ |
|
0.04043 |
0.00706 |
0.14808 |
0.03015 |
0.03587 |
-0.00328 |
| YD |
0.04088 |
|
0.06536 |
0.13184 |
0.05211 |
0.06440 |
0.03684 |
| GX |
0.00730 |
0.06593 |
|
0.11628 |
0.06263 |
0.00652 |
0.02926 |
| YN |
0.15081 |
0.13427 |
0.11799 |
|
0.19774 |
0.08288 |
0.17365 |
| SX |
0.03038 |
0.05293 |
0.06350 |
0.20091 |
|
0.06595 |
-0.00005 |
| LN |
0.03679 |
0.06501 |
0.00690 |
0.08386 |
0.06712 |
|
0.04311 |
| HLJ | -0.00332 | 0.03735 | 0.03007 | 0.17688 | -0.00016 | 0.04426 |
Locations: Suizhou (SZ), Yidu (YD), Guangxi (GX), Yunnan (YN), Shaanxi (SX), Liaoning (LN) and Heilongjiang (HLJ). Fst and Nst are above and below the diagonal, respectively. Negative values indicate that more nucleotide substitutions occur within than between populations.
To assess possible factors that might affect gene flow, an analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) was computed among populations. With the introduction of three-levels in the analysis, it was shown that 92.4% of the variance was distributed within populations and only 7.6% among populations (Table 6). The average Fst within seven populations (0.0759) was greatest compared with an Fst value among groups of 0.0143, and an Fst among populations within groups of 0.0655.
Table 6.
Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) for seven populations of Haemonchus contortus from China
| Variance component | Variance | % of total | P | F-statistic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among populations |
0.4007 |
7.59 |
|
|
| Within populations |
4.8814 |
92.41 |
0.00b |
Fst = 0.0759 |
| Among groupsa |
0.0759 |
1.43 |
0.32 |
Fct = 0.0143 |
| Within groupsa | 0.3423 | 6.46 | 0.00b | Fsc = 0.0655 |
aThe populations from the six provinces were divided into three groups according to their geographical origins, including Southwest (Guangxi and Yunnan), Central (Suizhou, Yidu and Shaanxi) and Northeast (Liaoning and Heilongjiang) in China.
bP < 0.05.
Fst values were also calculated between samples from China and those from each of the other four countries, including Italy, Malaysia, the USA and Yemen, for which nad4 sequence data were available. The results revealed that the highest level of genetic differentiation was recorded between China and the USA, with an Fst value of 0.41294 (Table 2). Moderate levels of genetic differentiation were recorded between China and Italy, or China and Yemen, with the Fst values of 0.14407 and 0.26710, respectively. The lowest level of differentiation was found between China and Malaysia, with an Fst value of 0.05841 (Table 2).
Discussion
In the present study, the ITS-2 and partial nad4 sequences were determined from 152 individual H. contortus specimens from seven populations of China. The ITS-2 sequences from these worms confirmed their specific identity as H. contortus. Further analysis revealed sequence variation of 2.6% in ITS-2 among all 152 individual worms from all locations in China. This magnitude of variation is consistent with variation (2.6%) detected in H. contortus populations in various countries, such as Germany and Sweden/Kenya [25,26], but lower than that (5.2%) detected between or among populations from seven countries, including Australia, France, Germany, New Zealand, Switzerland, The Netherlands and the UK [11]. For nad4, the nucleotide diversities within each of the seven H. contortus populations in China ranged from 0.018 to 0.037, with an average nucleotide diversity of 0.027 (Tables 2 and 4), which is in accordance with previously published data for this mitochondrial gene in various countries including Italy (0.026-0.03), Malaysia (0.032-0.044), the USA (0.024-0.03) and Yemen (0.021-0.036) [5,8,10]. Similarly, the high degree of diversity (i.e. 142 distinct haplotypes representing 152 individuals) and a mean haplotype diversity of 0.996 were in accordance with previous studies of the trichostrongyloids, such as Haemonchus placei and Teladorsagia circumcincta[7,27,28].
The present phylogenetic analysis revealed that there was no clear grouping of H. contortus according to host species (Additional file 2: Figure S1), a finding supported by the lack of significant differences in pairwise Fst and Nst values between H. contortus populations from LN or HLJ (sheep) and those from SZ, YD, GX, YN and SX (goat) (see Table 5). This result is similar to findings of previous studies, showing a limited relationship of H. contortus populations with different ruminant species in Brazil, Italy, Malaysia and Yemen [8-10].
The genetic analysis of the nad4 gene in the present study showed that the majority (92.4%) of genetic diversity was partitioned within populations of H. contortus from China, with no clear phylo-geographic structuring (with the exception of a subset of seven specimens from Yunnan), suggesting a high gene flow without clear geographical barriers among populations from different provinces. This proposal was supported by evidence of low pairwise Fst values between Chinese populations. The greatest nucleotide diversity within the H. contortus population from Yunnan, and the highest Fst values between this population and other Chinese populations, might relate to the fact that this province is particularly mountainous throughout, possibly preventing dispersal and gene flow.
On the other hand, on a global scale, the highest Fst value between H. contortus from China and the USA indicated a high genetic differentiation and less gene flow between these populations from two distinct continents. In contrast, the lowest genetic differentiation of Chinese specimens from those from Malaysia was reflected in the lowest pairwise Fst value. These results support a previous proposal that the global population genetic structure of H. contortus is characterized by no or low genetic differentiation between specimens from abutting geographical regions or within continents with limited barriers to gene flow, but significant genetic differentiation on a global scale (across continents) with substantial barriers to gene flow [7].
Previous studies have attributed a high degree of sequence diversity in the nad4 within populations of H. contortus to a large effective population size (Ne), high biotic potential, rapid, direct life-cycle and a high mutation rate in this polymorphic nematode [6,9,29], which explains the population genetic characteristics in China. In this country, haemonchosis is widespread geographically, and the prevalence and intensity of H. contortus infection are relatively high. An appraisal of key studies published in Chinese [30-34] shows that H. contortus exists in at least 30 of the 32 provinces in China, and is the dominant intestinal parasitic nematode of sheep and goats, with prevalences ranging from 6.5% to 100% and infection intensities of at least 20–8000 worms per host. The movement of livestock throughout China is also common. Since 1978, the livestock industry has undergone an enormous transformation. By the end of 1996, the total numbers of goats and sheep reached 303 million head, and the number has increased by 78.5% since that time, with a high demand on the red meat market for lamb [35]. Taken together, these findings indicate that the population genetic characteristics of H. contortus in China appear to be similar to those in other countries and studies.
As there is no commercial vaccine against haemonchosis in China, like elsewhere, the control of H. contortus relies largely on anthelmintics [36]. Here, the most widely used anthelmintics are albendazole, mebendazole, levamisole and ivermectin [36]. In spite of the apparently excessive use of anthelmintics against trichostrongyloids [36], no precise information is available on the nature and extent of drug resistance in H. contortus in China. Nonetheless, there are a small number of studies [37-39] reporting drug resistance against benzimidazoles and ivermectin in H. contortus populations in China. As the level of gene flow among populations of H. contortus parasitizing goats and sheep in China was shown here to be very high, there is substantial opportunity for rare resistance alleles to spread, indicating an urgent need to conduct a nationwide investigation of drug resistance in H. contortus. Such a focus will inform the scientific and non-scientific communities about the prevalence and intensity of resistance, and should underpin future control efforts in China.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this is the first study of genetic variation within H. contortus in China. The results revealed high within-population variation, low population genetic differentiation and high gene flow of H. contortus in China. The results also indicated that on a global scale, there is no or a low level of genetic differentiation among H. contortus populations from the same continent, and significantly higher levels of genetic differentiation among those from different continents. These findings have important implications for studying the molecular epidemiology and controlling the spread of anthelmintic resistance against H. contortus in China.
Abbreviations
AMOVA: Analysis of molecular variance; ITS-2: The second internal transcribed spacer of ribosomal DNA; L3s: The third-stage larvae; MJ: Median joining; ML: Maximum likelihood; MP: Maximum parsimony; nad4: Mitochondrial nicotinamide dehydrogenase subunit 4 gene; Ne: A large effective population size; NJ: Neighbour-joining; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
MH conceived the project. MB, WH, FZ, GZ, CW, XY, YZ, JZ, RF collected samples. FY and FL carried out laboratory work. FY performed the data analyses. FY and MH interpreted the data. FY, RBG and MH wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Alignment of the 18 unique ITS-2 sequence types representing 152 individual adults of Haemonchus contortus from seven different geographical locations in China. The accession number for each sequence is given in Table 3.
The neighbor-joining (NJ) tree displaying the relationship among the 142 nad4 sequence types representing 152 individual adults of Haemonchus contortus from seven different geographical locations in China. Each terminal branch represents one sequence. Each individual sequence is labeled according to geographical origin of the worm from which it was derived. Bootstrap values of >50% are indicated above or below the branches. Haemonchus placei (accession no. AF70785) was used as the outgroup.
Contributor Information
Fanyuan Yin, Email: yinfangyuan96@126.com.
Robin B Gasser, Email: robinbg@unimelb.edu.au.
Facai Li, Email: li78561270@163.com.
Min Bao, Email: baomin9999@163.com.
Weiyi Huang, Email: wyhuang@gxu.edu.cn.
Fengcai Zou, Email: zfc1207@126.com.
Guanghui Zhao, Email: zgh083@nwsuaf.edu.cn.
Chunren Wang, Email: chunrenwang@sohu.com.
Xin Yang, Email: 695237569@qq.com.
Yanqin Zhou, Email: yanqinzhou@mail.hzau.edu.cn.
Junlong Zhao, Email: zhaojunlong@mail.hzau.edu.cn.
Rui Fang, Email: fangrui19810705@163.com.
Min Hu, Email: mhu@mail.hzau.edu.cn.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr Wenbiao Jiao for assistance with analyses. This study was supported by the “Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest” (Grant no. 201303037) and the “Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (Program no. 2011PY118) to MH. Funding from the Australian Research Council (ARC), the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) and Melbourne Water Corporation is gratefully acknowledged (RBG).
References
- O’Connor LJ, Walkden-Brown SW, Kahn LP. Ecology of the free-living stages of major trichostrongylid parasites of sheep. Vet Parasitol. 2006;142:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.08.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaou S, Gasser RB. Prospects for exploring molecular developmental processes in Haemonchus contortus. Int J Parasitol. 2006;36:859–868. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser RB, Bott NJ, Chilton NB, Hunt P, Beveridge I. Toward practical, DNA-based diagnostic methods for parasitic nematodes of livestock-bionomic and biotechnological implications. Biotechnol Adv. 2008;26:325–334. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller JE, Horohov DW. Immunological aspects of nematode parasite control in sheep. J Anim Sci. 2006;84:E124–E132. doi: 10.2527/2006.8413_supple124x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin MS, Yowell CA, Courtney CH, Dame JB. Host movement and the genetic structure of populations of parasitic nematodes. Genetics. 1995;141:1007–1014. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson TJC, Blouin MS, Beech RN. Population biology of parasitic nematodes: applications of genetic markers. Adv Parasitol. 1998;41:219–283. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troell K, Engstrom A, Morrison DA, Mattsson JG, Hoglund J. Global patterns reveal strong population structure in Haemonchus contortus, a nematode parasite of domesticated ruminants. Int J Parasitol. 2006;36:1305–1316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti MC, Citterio CV, Bazzocchi C, Epis S, D’Amelio S, Ferrari N, Lanfranch P. Genetic variability of Haemonchus contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongyloidea) in alpine ruminant host species. J Helminthol. 2010;84:276–283. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X09990587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasil BSAF, Nunes RL, Bastianetto E, Drummond MG, Carvalho DC, Leite RC, Molento MB, Oliveira DAA. Genetic diversity patterns of Haemonchus placei and Haemonchus contortus populations isolated from domestic ruminants in Brazil. Int J Parasitol. 2012;42:469–479. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2012.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharamah AA, Siti Azizah MN, Rahman WA. Genetic variation of Haemonchus contortus (Trichostrongylidae) in sheep and goats from Malaysia and Yemen. Vet Parasitol. 2012;188:268–276. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser RB, Zhu XQ, Chilton NB, Newton LA, Nedergaard T, Guldberg P. Analysis of sequence homogenization in rDNA arrays of Haemonchus contortus by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 1998;19:2391–2395. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150191405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt PW, Knox MR, Le Jambre LF, McNally J, Anderson LJ. Genetic and phenotypic differences between isolates of Haemonchus contortus in Australia. Int J Parasitol. 2008;38:885–900. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang XJ, Huang JX, Yang JZ, Sun RY, Zhang HF, Liu EY. Studies on the simultaneous diagnosis of haemonchosis and fascioliasis in cattle and sheep by Dot-ELISA. Acta Agr Zhejiang. 1997;9:97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wei CY, Sun LJ, Lin Q. Preliminary investigation on prevalence of parasites in sheep in Yuyang District in Yulin City. J Anim Sci Vet Med. 2013;32:1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenfels JR, Pilitt PA, Hoberg EP. New morphological characters for identifying individual specimens of Haemonchus spp. (Nematoda: Trichostrongyloidea) and a key to species in ruminants of North America. J Parasitol. 1994;80:107–119. doi: 10.2307/3283353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser RB, Chilton NB, Hoste H, Beveridge I. Rapid sequencing of rDNA from single worms and eggs of parasitic helminthes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993;21:2525–2526. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson LA, Chilton NB, Gasser RB. Differentiation of Haemonchus placei from H. contortus (Nematoda: Trichostrongylidae) by the ribosomal DNA second internal transcribed spacer. Int J Parasitol. 1995;25:483–488. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(94)00156-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–2739. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Librado P, Rozas J. DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1451–1452. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics. 1989;123:585–595. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu YX. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics. 1997;147:915–925. doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.2.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics. 1992;131:479–491. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandelt H, Forster P, Rohl A. Median joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol. 1999;16:37–48. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heis M, Epe C, Schnieder T. Differences in the second internal transcribed spacer (ITS-2) of eight species of gastrointestinal nematodes of ruminants. J Parasitol. 1999;85:431–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troell K, Mattsson JG, Alderborn A, Höglund J. Pyrosequencing analysis identifies discrete populations of Haemonchus contortus from small ruminants. Int J Parasitol. 2003;336:765–771. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(03)00068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin MS, Yowell CA, Courtney CH, Dame JB. Substitution bias, rapid saturation, and the use of mtDNA for nematode systematics. Mol Biol Evol. 1998;15:1719–1727. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braisher TL, Gemmell NJ, Grenfell BT, Amos W. Host isolation and patterns of genetic variability in three populations of Teladorsagia from sheep. Int J Parasitol. 2004;34:1197–1204. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2004.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blouin MS, Dame JB, Tarrant CA, Courtney CH. Unusual population genetics of a parasitic nematode: mtDNA variation within and among populations. Evolution. 1992;46:470–476. doi: 10.2307/2409865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zong ZJ, Wang ZM, Shi JH, Si QZRG, Zhao RGT. Seasonal dynamic observation of Haemonchus contortus, Nematodirus, Oesophagostomum and their parasitic stage larvae. Chin J Vet. 1997;23:30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yang SW. The measures of prevention and control of parasitosis of goats in Youyang. Livest Market. 2005;8:23–24. [Google Scholar]
- He SW, Li F, Liu W, Xie ZK, Liu Y. Survey on parasites infection among goats in Xiangxi, Hunan Province. Chin J Vet Parasitol. 2008;16:16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ding YL, Wang R, Wang ZB, Du CC, Yang XY, Wang JL, Zhu ML, Liu XG, Jiao GY, Guo Y, Wang FL. Investigation of gastrointestinal parasite infection from goats in loess plateau area of Shanxi Province. Heilongjiang Ani Sci Vet Med. 2010;6:115–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang DS, He Q, Feng Y, Li FY. The survey report of parasite among cattle in Tongjiang County. Livest Poultry Ind. 2012;282:79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Xu XG, Chen J, Li J. The developmental course and characteristics of livestock industry in China. Chin J Livest. 2011;47:15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gan SB. Current situation of anti-parasite drug in China. Chi J Parasit Dis Con. 2005;18:401–403. [Google Scholar]
- He GS, Gu YX, Cao J, Zhu SH, Wang Q, Xu MQ. Detection of anthelmintic resistance against Haemonchus contortus in goats using the egg hatch test. Chin J Vet Parasitol. 1999;7:8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pu WB, Yue C. Detection on the sheep resistance of gastrointestinal nematode against albendazole in Urumqi area. Xinjiang Agr Sci. 2009;46:217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan ZY The resistance detection of nematodes from sheep gastrointestinal under different cultivate pattern Master’s Degree Thesis 2010. 24127347
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Alignment of the 18 unique ITS-2 sequence types representing 152 individual adults of Haemonchus contortus from seven different geographical locations in China. The accession number for each sequence is given in Table 3.
The neighbor-joining (NJ) tree displaying the relationship among the 142 nad4 sequence types representing 152 individual adults of Haemonchus contortus from seven different geographical locations in China. Each terminal branch represents one sequence. Each individual sequence is labeled according to geographical origin of the worm from which it was derived. Bootstrap values of >50% are indicated above or below the branches. Haemonchus placei (accession no. AF70785) was used as the outgroup.