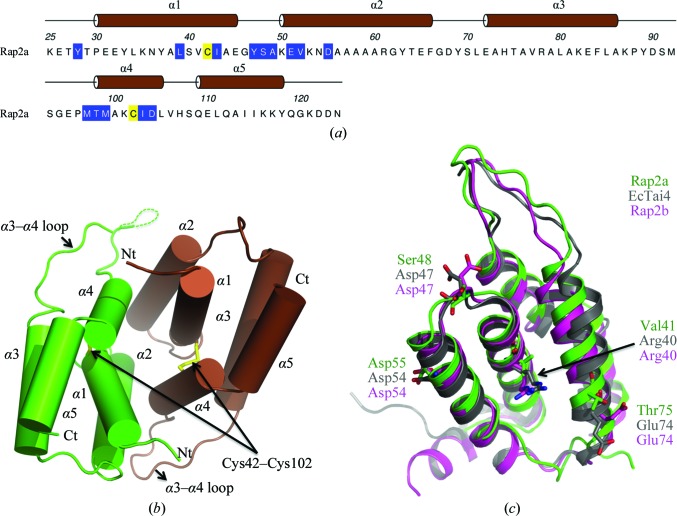
Figure 6.
Primary, secondary and tertiary structure of Rap2a. (a) The amino-acid sequence with assigned secondary structure and helices numbered. Residues involved in disulfide-bond formation are coloured yellow and residues involved in subunit–subunit interactions are shown on a blue background. (b) Cartoon representation of the Rap1a dimer with subunits coloured brown and green. The disulfides and the N- and C-termini are labelled. (c) Cartoon representation of Rap2b (pink) and EcTai4 (grey) superimposed on Rap2a (green). Asp54 and Asp47 are involved in the hydrogen-bond network in the interface in EcTai4 and are absolutely conserved in Rap2b; in Rap2a, Asp47 is replaced by Ser48. Arg40 and Glu74 (replaced by Val41 and Thr75, respectively, in Rap2a) have been shown to play a major role in binding to EcTae4; both of these residues are also conserved in Rap2b but not in Rap2a.