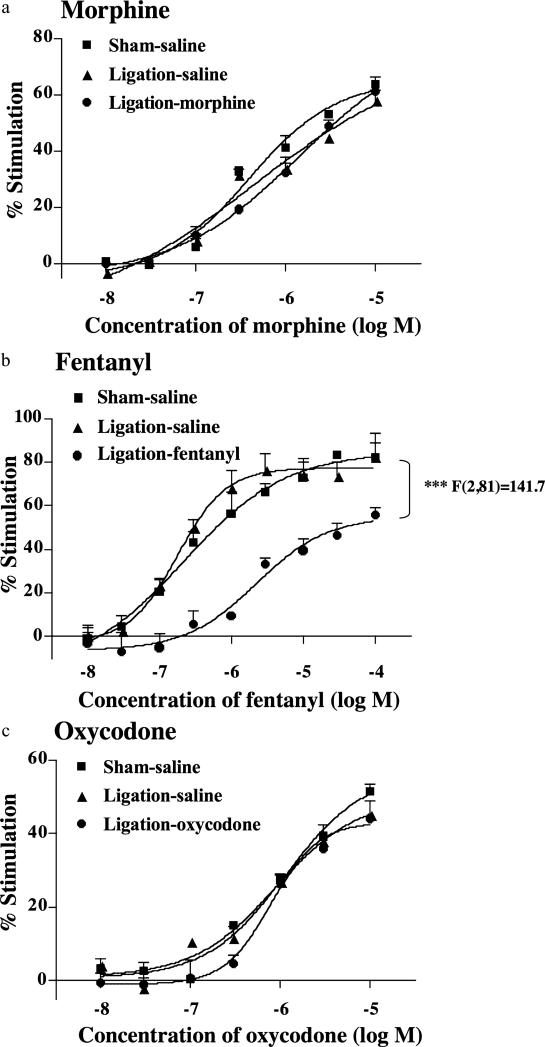
Figure 3.
Effect of repeated injection of morphine (a), fentanyl (b) or oxycodone (c) on the morphine-, fentanyl- or oxycodone-induced increase in [35S] GTPgS binding to membranes of the ipsilateral side of the spinal cord obtained from sham-operated and sciatic nerve-ligated ICR mice. Repeated s.c. injection of saline, morphine, fentanyl or oxycodone was started 7 days after sciatic nerve ligation. ICR mice were repeatedly injected with saline, morphine, fentanyl or oxycodone once a day for 14 consecutive days. During the first 6 days after surgery, mice were not treated with saline, morphine, fentanyl or oxycodone. Membranes were prepared at 21 days after nerve ligation. Each value represents the mean ± standard error of the mean of four samples