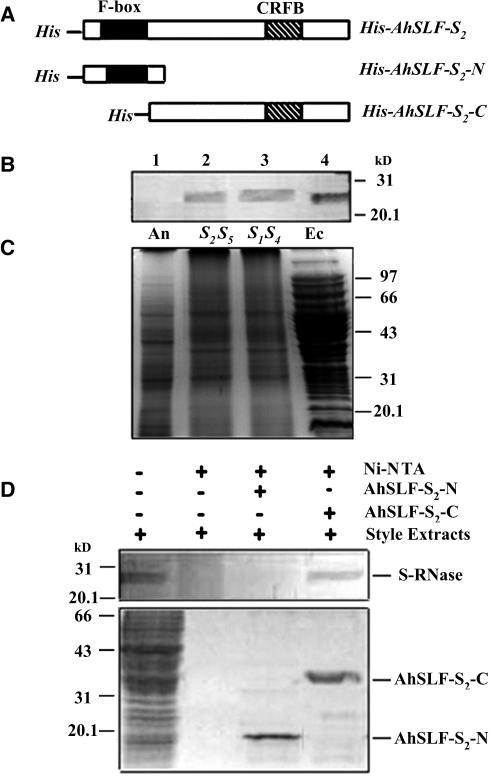
Figure 1.
Pull-Down Assay for the Physical Interaction between AhSLF-S2 and S-RNases.
(A) Constructs used for expressing the His-tagged products from the full-length AhSLF-S2 (His-AhSLF-S2) and the N-terminal (His-AhSLF-S2-N) and C-terminal (His-AhSLF-S2-C) regions. CRFB represents a conserved domain found among similar F-box proteins to AhSLF-S2 in Arabidopsis (Kuroda et al., 2002).
(B) Immunoblot detection of S-RNases from total proteins of Antirrhinum anther (lane 1), styles of S2S5 (lane 2) and S1S4 (lane 3), and E. coli expressing S2-RNase (lane 4) by a polyclonal antibody against S2-RNase. Fifty micrograms of total proteins were loaded in each lane.
(C) The proteins also were stained by Coomassie blue for loading control. An, anther; Ec, proteins from bacteria expressing S2-RNase; S2S5, style of S2S5; S1S4, style of S1S4.
(D) A pull-down assay for AhSLF-S2 interaction with S-RNase. Ni-NTA resin and the purified fusion proteins of His-AhSLF-S2-N and His-AhSLF-S2-C were incubated with the extracts of Antirrhinum styles of S2S5. Bound proteins were pulled down with His-NAT resin, eluted with lysis buffer, separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, transferred to membranes, and analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-S-RNase antibody (top panel). Input proteins after washing also were stained by Coomassie blue (bottom panel). Style total proteins were used as a positive control. Molecular mass markers are indicated in kilodaltons.