Figure 5.
AhSLF-S2 Interacts with ASK1- and CUL1-Like Proteins.
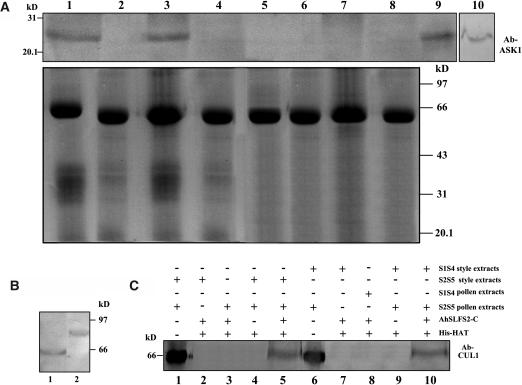
(A) Extracts of styles of S1S4 or S2S5 lines (50 μg each) and pollen of an S2S5 line (50 μg) were coimmunoprecipitated with anti-AhSLF-S2-C antibody (3 μL) (lanes 1 and 3) or control preimmune serum (3 μL) (lanes 2 and 4), respectively. As additional controls, the extracts of styles of S1S4 (lane 5) and S2S5 (lane 6) lines or pollen of S1S4 (lane 7) and S2S5 (lane 8) lines also were coimmunoprecipitated with anti-AhSLF-S2-C antibody (3 μL). After immunoprecipitation, the proteins were subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE followed by protein gel blotting with specific antibodies against AtASK1 of Arabidopsis (top panel). Total proteins of Antirrhinum pollen (lane 9) and Arabidopsis leaf (lane 10) also were used as positive controls. The bottom panel represents the Coomassie blue–stained gel before protein gel blotting for equal loading of proteins.
(B) Immunoblot detection of CUL1-like protein from total pollen proteins of Antirrhinum pollen (lane 1) and Arabidopsis (lane 2).
(C) A pull-down assay for an interaction between AhSLF-S2 and CUL1-like proteins. His-NAT resin or the purified fusion proteins of His-AhSLF-S2-C were incubated with the extracts of Antirrhinum styles from S2S5 and pollen of S2S5 or S1S4 (lanes 5 and 10), respectively. The extracts of the Antirrhinum styles from S2S5 and pollen of S2S5 or S1S4 were incubated without His-AhSLF-S2-C as negative controls (lanes 4 and 9), and style and pollen extracts were used as positive controls (lanes 1 and 6). As additional controls, the extracts of the styles of S2S5 (lane 2) and S1S4 (lane 7) lines or pollen of S2S5 (lane 3) and S1S4 (lane 8) lines were incubated with anti-AhSLF-S2-C antibody (3 μL). Proteins bound were pulled down with His-NAT resin, eluted with lysis buffer, separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, transferred to membranes, and analyzed by immunoblotting with Arabidopsis anti-CUL1 antibody.