Figure 3.
Characterization and Knockdown of Zebrafish Orthologs of KLHL41
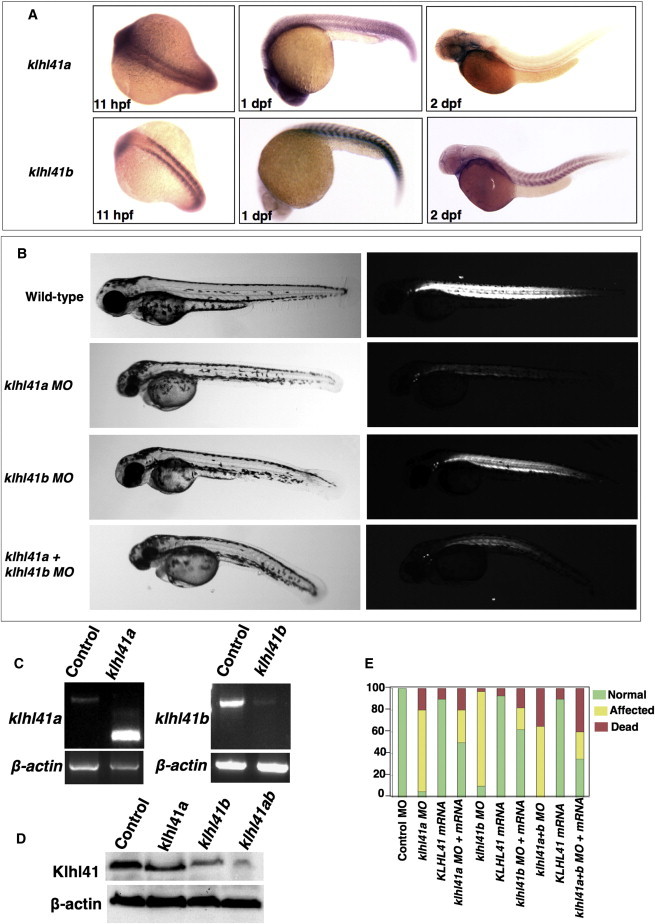
(A) In situ hybridization of the zebrafish Klhl41 genes shows early expression during myogenesis in developing somites (11 hr after fertilization). Klhl41a is expressed in brain, eyes, and muscle at 1 dpf. Later in development expression is largely restricted to brain and heart (2 dpf), although low levels of expression in axial slow skeletal myofibers cannot be excluded due to limited sensitivity of the assay. Klhl41b expression is localized to skeletal muscle and heart at all developmental stages (1–2 dpf).
(B) Knockdown of Klhl41 genes in zebrafish using antisense morpholinos results in myopathic changes. Live microscopy of zebrafish embryos at 3 dpf reveals leaner and smaller bodies in comparison to wild-type (WT) fish. Under polarized microscopy, zebrafish embryos exhibit a reduction in birefringence in morphant fish, quantified in ImageJ as described (WT controls: 100% ± 5.9% klhl41a: 23% ± 3.0%; klhl41b: 31% ± 8.2%; klhl41ab: 16% ± 4.2%). Double knockdown fish show a more severe skeletal muscle phenotype than single morphants.
(C) RT-PCR analysis showed knockdown of normal transcripts in the morphant fish.
(D) Immunoblot analysis showed reduction in Klhl41 levels in klhl41a, klhl41b, and klhl41ab fish. Klhl41 antibody recognizes both klhl41a and klhl41b and therefore show immunoreactibility to the other gene in the single morphants that is highly reduced in double morphants.
(E) Overexpression of human KLHL41 mRNA restores the skeletal muscle phenotypes of klhl41a/b single and double morphants suggesting morpholino specificity. The mRNA concentration used to rescue were as follows: klhl41a (50 pg), klhl41b (75 pg), klhl41a+b (60 pg of each).
