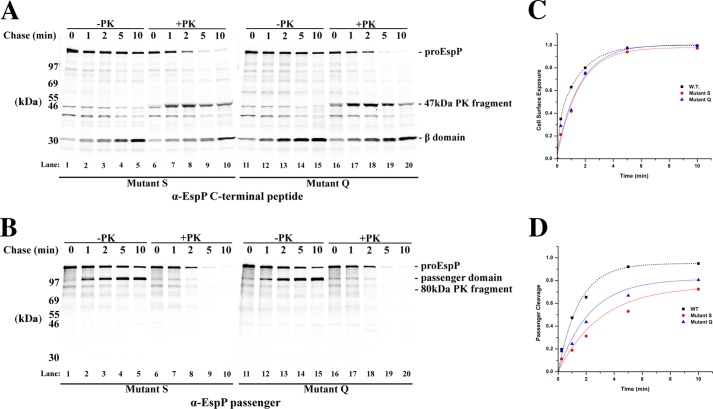
FIGURE 6.
EspP mutants S and Q display only moderate passenger domain translocation defects. A and B, AD202 cells transformed with pRLS5 or a derivative encoding mutant S or Q were subjected to pulse-chase labeling following the addition of IPTG. Half of each culture sample was treated with PK, and immunoprecipitations were conducted using antisera generated against an EspP C-terminal peptide (A) or the EspP passenger domain (B). C and D, the fraction of the passenger domain that was surface-exposed and released by proteolytic cleavage at each time point in A is shown. For comparison, the results obtained in the experiment shown in Fig. 2 in which we analyzed the assembly of wild-type EspP are also plotted.