FIGURE 1.
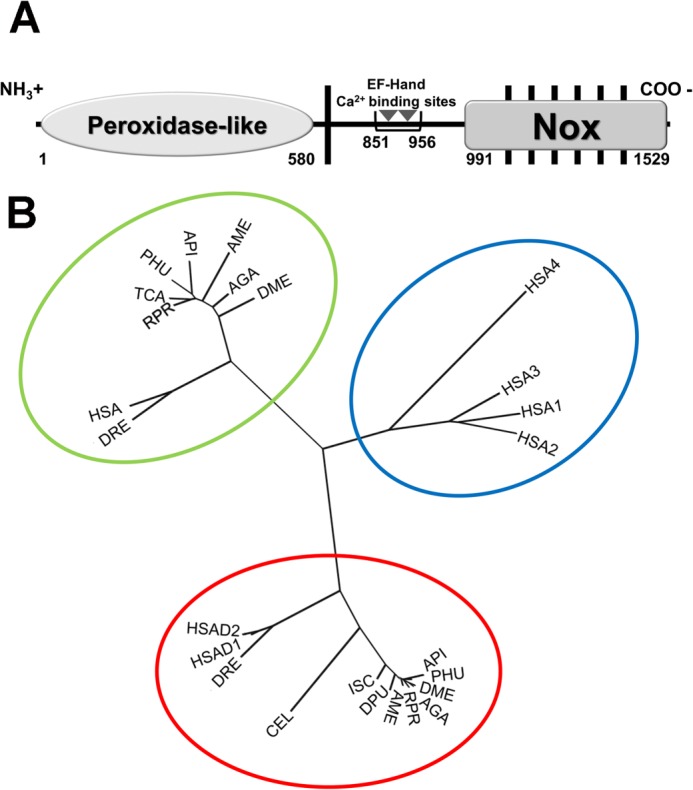
Structure and phylogeny relationships of R. prolixus dual oxidase. A, the scheme shows the positions of the predicted peroxidase-like and NOX domains, transmembrane α-helices (black bars), and cytosolic EF-hand calcium-binding sites (gray triangles) of R. prolixus dual oxidase (RpDuox). B, phylogenetic comparisons between NOX (1–5) sequences and the sequences of Duox NOX domains. The following species were used for tree construction. The Duox sequences were: RPR, R. prolixus; HSAD1, H. sapiens Duox1; HSAD2, H. sapiens Duox2; CEL, C. elegans; DRE, D. rerio; API, A. pisum; DME, D. melanogaster; AME, A. mellifera; DPU, D. pulex; ISC, I. scapularis; AGA, A. gambiae (gi 158298988) and PHU, P. humanus corporis. The NOX5 sequences were: RPR, R. prolixus; HSA, H. sapiens; DRE, D. rerio; API, A. pisum; TCA, T. castaneum; DME, D. melanogaster; AME, A. mellifera; PHU, P. humanus corporis and AGA, A. gambiae. The NOX1–4 sequences were: HSA1, H. sapiens NOX1; HSA2, H. sapiens NOX2; HSA3, H. sapiens NOX3 and HSA4, H. sapiens NOX4. Colored ellipses indicate the three NOX clusters, vertebrate specific NOX1–4 (blue), NOX5 (green), and Duox (red).
