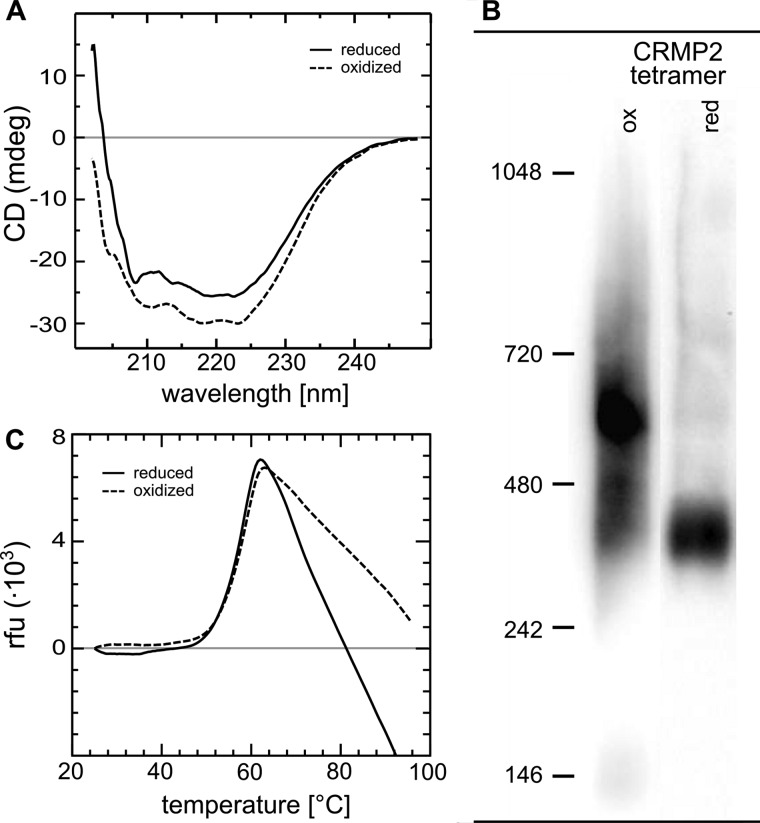
FIGURE 3.
Conformational changes of CRMP2 upon reduction. A, CD spectroscopy of oxidized and subsequently reduced CRMP2. The decrease in ellipticity between 210–220 nm indicates a decrease in α-helical content of reduced CRMP2. B, blue native gel electrophoresis of reduced and oxidized tetrameric CRMP2. 1 μg of the protein was reduced by a catalytic amount of Grx2c (1:100, +DTT+TCEP) or oxidized by H2O2 treatment. Both fractions were analyzed by blue native gel electrophoresis. The higher migration velocity of reduced CRMP2 indicated binding of more Coomassie dye molecules and thus the exposure of more hydrophobic surfaces compared with the oxidized CRMP2 tetramer. The marks depicted were introduced only for orientation purposes and do not reflect the actual molecular weight of the complexes (see Fig. 1). C, differential scanning fluorimetry of reduced and oxidized CRMP2. No significant differences were observed in the thermal stability of reduced and oxidized CRMP2.