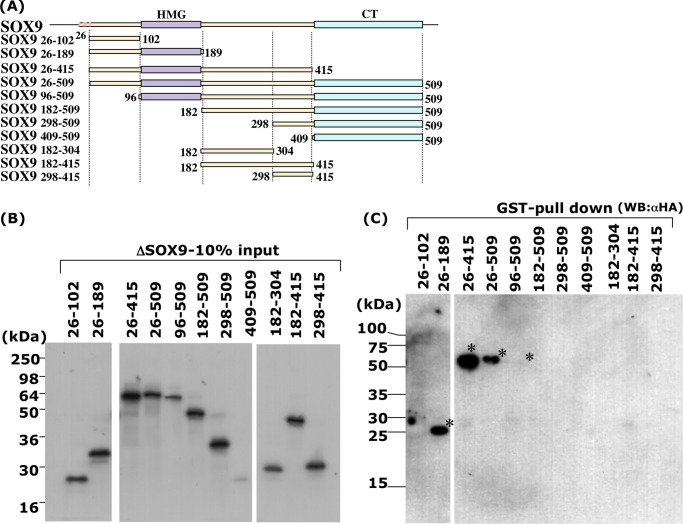
FIGURE 2.
In vitro association of SOX9 and E6-AP. Several truncated SOX9 protein fragments were generated by in vitro translation as described previously (23), applied onto SDS-PAGE, and detected by Western blotting using an HA antibody. A, schematic representation of N-terminal- or C-terminal-truncated SOX9 fragments. SOX9 consists of a high mobility group DNA-binding domain (HMG box), a C-terminal transactivation (CT) domain, and four ATG codons at the N terminus portion in-frame. Numbers indicate the location of the fragments in amino acid number from the N terminus. B, 10% of the input SOX9 proteins was applied to the gel. C, pull-down assay of SOX9 fragments with GST-E6-AP. Significant pull-down of SOX9 fragments (asterisk) was seen with SOX9 fragments 26–189, 26–415, 26–509, and 96–509, which contain amino acids 96–189, corresponding to the HMG domain.