FIGURE 1.
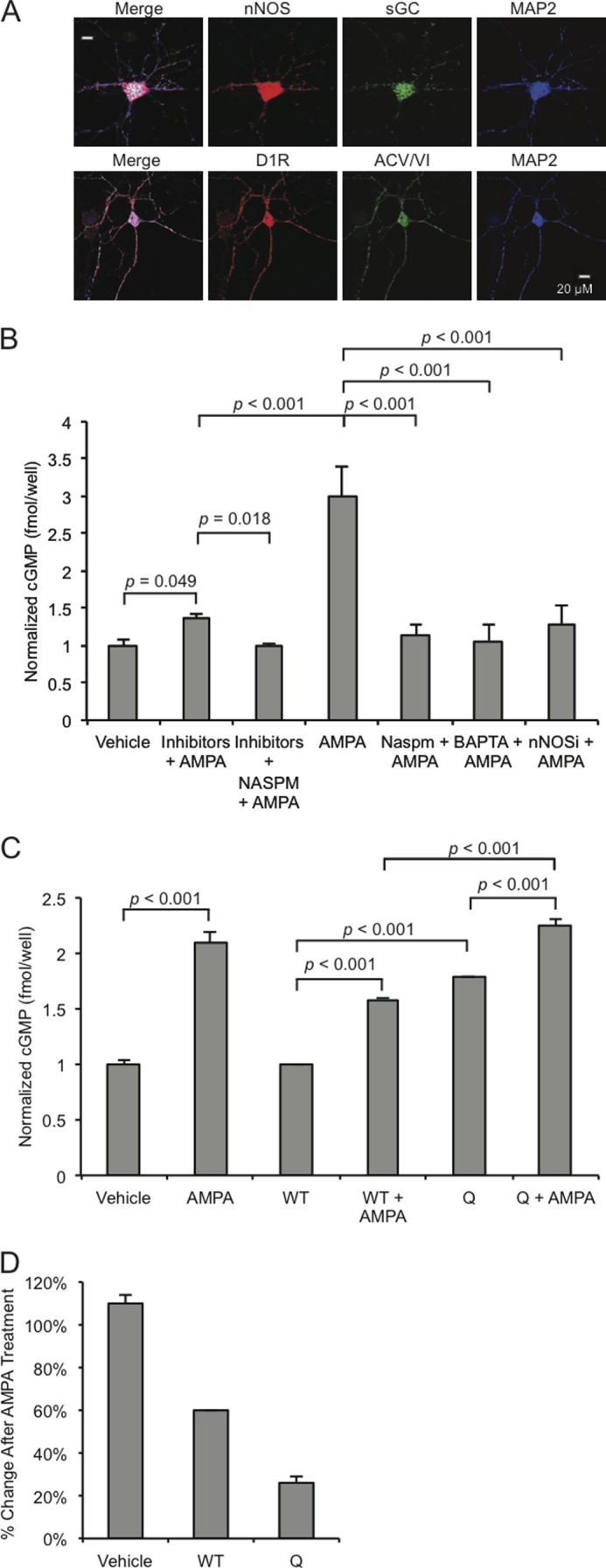
CPARs regulate cGMP production. A, accumbens MSNs (10 DIV) were stained for nNOS, adenylyl cyclase type VI (ACV/VI), soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC), D1Rs, and MAP2. B, MSNs were either treated with vehicle or AMPA or with a mixture of inhibitors (APV, 10 μm; CdCl2, 50 μm; TTX, 500 nm) or BAPTA (500 μm) or nNOS Inhibitor (2 μm) or NASPM (200 μm) and then with AMPA (50 μm, 1 min) in the indicated combinations, and cGMP concentrations were measured by ELISA. C, MSNs (10 DIV) were infected overnight with Sindbis viruses expressing wild type GluA2 (WT) or GluA2-Q (Q) and treated with AMPA (50 μm, 1 min) or treated with vehicle as indicated, and cGMP concentrations were measured by ELISA. D, corresponding relative percent changes in the three infection conditions after AMPA treatment. Concentrations are fmol/well with n = 6 wells/test condition. Inhibitors or antagonists were added 30 min before treatment, and virus infections were performed 12 h before lysis. Data are represented as the mean ± S.E. normalized to vehicle treatment and analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher's post hoc tests.
