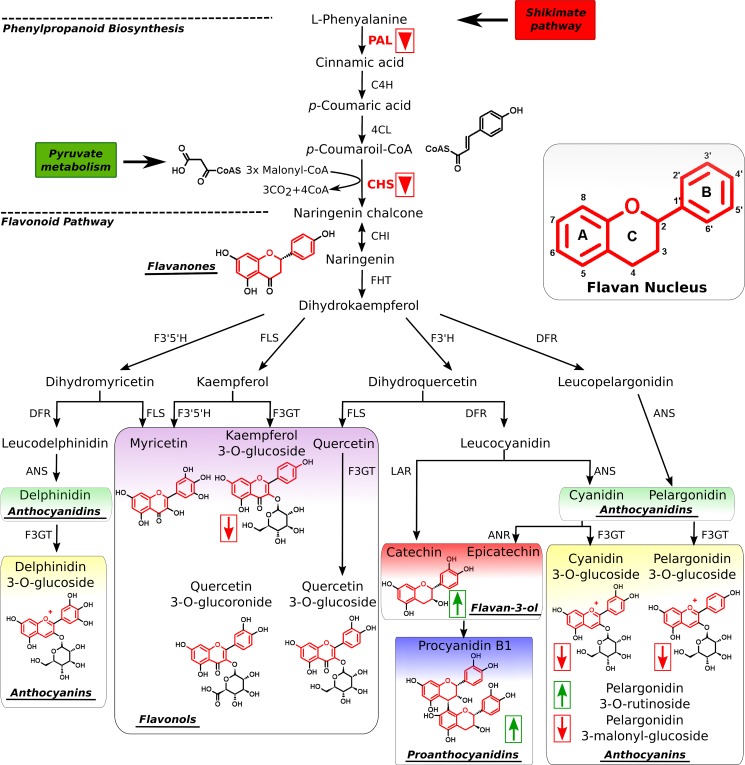
FIGURE 1.
The phenolic compound biosynthesis pathway. A schematic representation of the phenylpropanoid and flavonoid biosynthesis pathway is shown. Major families of flavonoid compounds are highlighted. Flavonoids are characterized by the presence of the flavan nucleus with A, B, and C rings as indicated (inset). Final products of the flavonoid pathway such as pelargonidin 3-O-glucoside, are often glycosylated at the position 3 of the C ring of the flavan nucleus. Suppression of Fra a protein expression affects the expression of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) and chalcone synthase (CHS) genes (red inverted triangles) and alters phenolic compound accumulation with an increase in the levels of catechin and a decreased accumulation of anthocyanins (as indicated by arrows) (28).