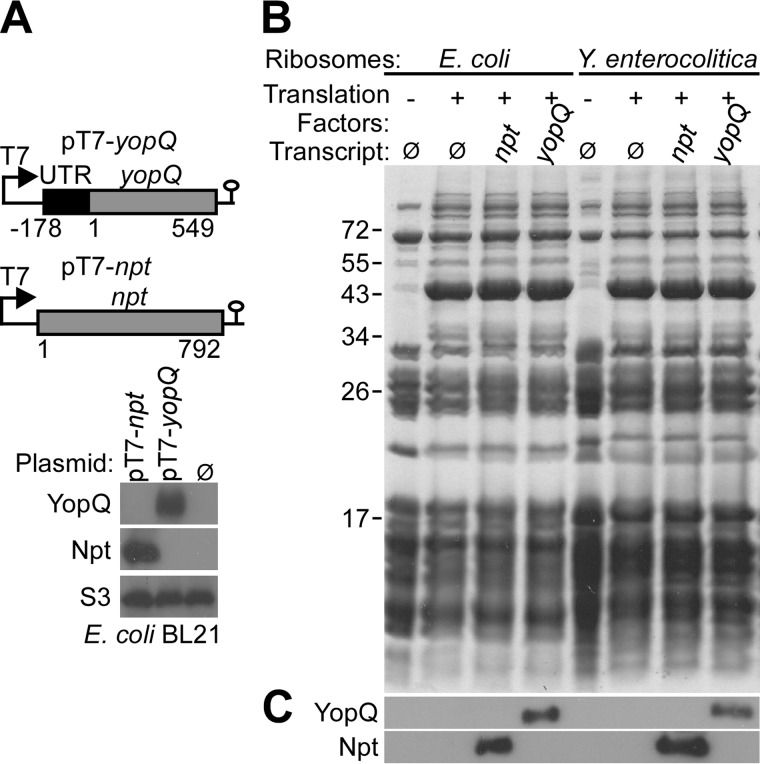
FIGURE 2.
In vivo and in vitro expression of yopQ. A, top panel, schematic of plasmids expressing yopQ or npt under control of the T7 promoter. Bottom panel, plasmids were transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3), and expression was induced by the addition of IPTG to induce T7 polymerase expression. Plasmid- or mock (Ø)-transformed bacteria were lysed, and cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with polyclonal antisera raised against YopQ or Npt as well as monoclonal antibody against ribosomal protein S3. B, ribosomes were isolated from E. coli BL21(DE3) and Y. enterocolitica W22703 lysates with hydrophobic interaction chromatography and sedimentation through 30% sucrose cushion. T7 polymerase derived yopQ and npt mRNA from pT7-yopQ and pT7-npt and in vitro translation system were used to measure translation by E. coli BL21(DE3) and Y. enterocolitica W22703 ribosomes. Translation reactions were analyzed by Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE. C, translation products were identified by immunoblotting with polyclonal antibodies against YopQ and Npt.