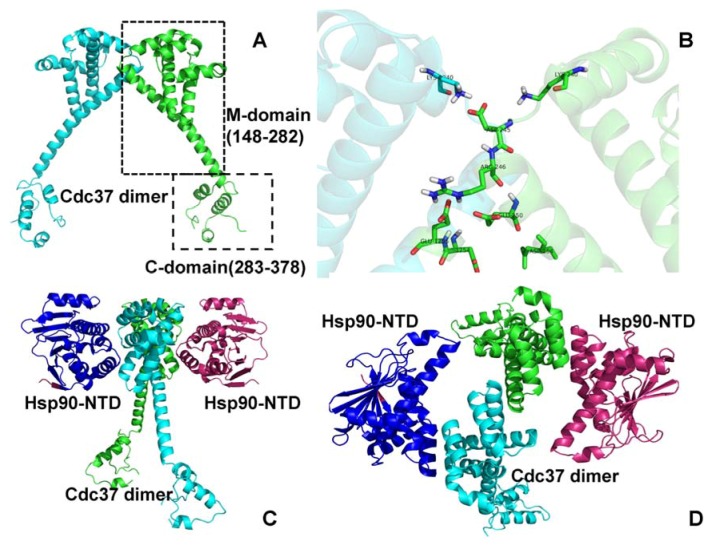
Figure 1.
Structural Characterization of the Cdc37 Chaperone. (A) The crystal structure of human Cdc37 dimer from the complex with the NTD of yeast Hsp90 (pdb id 1US7) [50]. The Cdc37 monomers are colored in cyan and green. The middle domain (residues 148–282) is involved in recognition of protein kinase clients. The C-terminal domain (residues 283–378) is involved in dimerization. (B) A close-up of the intermonomer interface from the crystal structure of the Cdc37 dimer [50]. The front view (C) and the top view (D) of the Cdc37 dimer (colored in green and cyan) bound to the NTDs of yeast Hsp90 (colored in blue and pink). The crystal structure of human Cdc37 dimer (pdb id 1US7) [50], the crystal structure of the isolated Cdc37 M-domain (pdb id 2W0G) [52] and the NMR structure of the complex of the human Cdc37 M-domain with the N-terminal domain of human Hsp90 (pdb id 2K5B) [52] have provided structural information used in this study.