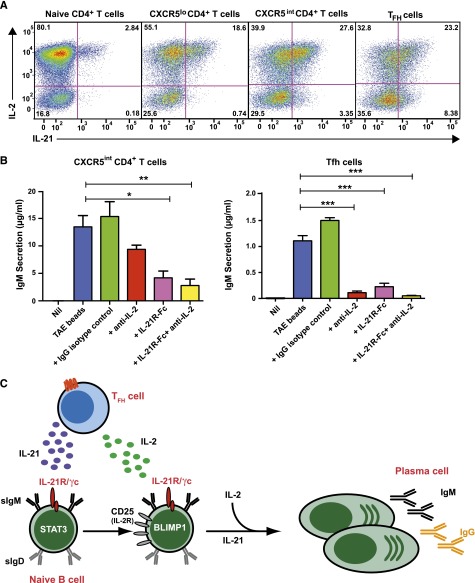
Figure 7.
IL-2 and IL-21 produced by Tfh cells cooperate to induce Ig secretion by co-cultured naïve B cells. (A) Naïve, CXCR5lo, CXCR5intermediate, and CXCR5hi Tfh CD4+ T cells were sort-purified from human tonsils and then stimulated in vitro with TAE beads. After 5 days, expression of IL-2 and IL-21 in these different populations following restimulation with PMA/ionomycin was determined. The values represent the proportions of cytokine-expressing cells. (B) CD4+CXCR5intermediate T cells and CXCR5hi Tfh cells were sorted from tonsil and co-cultured with autologous naïve B cells either in the absence (Nil) or presence of TAE beads (blue). Endogenous IL-2 and/or IL-21 were neutralized by the addition of anti-IL-2 mAb (red), IL-21R-Fc (pink), or anti-IL-2 mAb plus IL-21R-Fc (yellow), respectively. An isotype control mAb (green) was also included. IgM secretion was measured after 9 days. Results represent 2 independent experiments performed using cells from different donor tonsils. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .0001. (C) IL-21, secreted from Tfh cells, promotes B-cell maturation by inducing Blimp-1. IL-21 also enhances CD25 expression on naïve B cells, sensitizing them to the effects of IL-2, which is also secreted by Tfh cells. IL-2 then enhances the effects of IL-21 on B cells. IL-21 and IL-2 thus work cooperatively to induce plasma cell development and Ig secretion.