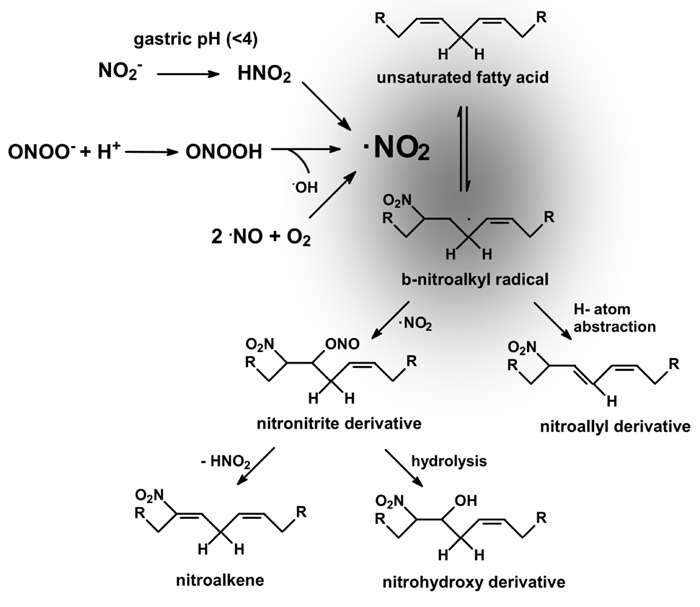
Figure 1. Mechanisms of unsaturated fatty acid nitration. Nitrogen dioxide can be formed by at least three major biologically relevant mechanisms (see text) and react with unsaturated fatty acids to preferentially form (at low oxygen tensions) nitro-alkenes (nitro group bonded at the double bond) and nitro-allyl derivatives (nitro group bonded at a single bond). NO2-FA alkylates susceptible thiols of multiple transcriptional regulatory proteins, affecting downstream gene expression and the metabolic and inflammatory responses under their regulation.