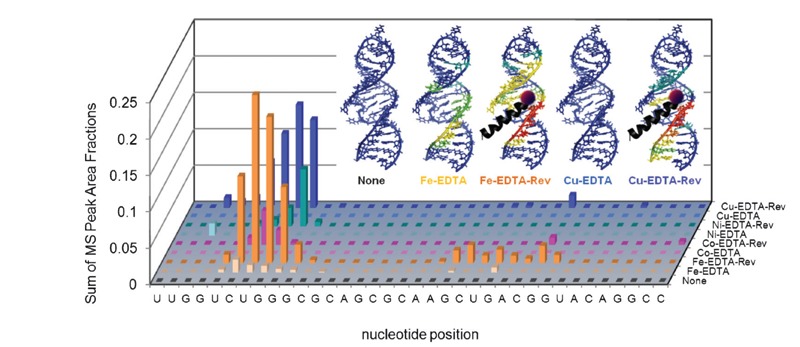
Figure 8. Targeted cleavage of Rev response element (RRE) RNA required attachment of catalysts to the Rev peptide in order to achieve efficient cleavage, as seen by differences in reactivity between the M-chelate-Rev catalysts and M-chelates lacking Rev (56). After 1 h incubation of each catalyst and co-reactants with the Fl-RRE RNA, the apparent abundances of individual RNA cleavage fragments were quantified. The data correspond to the abundances (MS peak area fractions) of oxidation products (cleavage fragments containing nascent terminal 3′-PO4, 3′-PG, or 5′-PO4 overhangs), at positions corresponding mechanistically (adjacent) to each illustrated site of H-abstraction, after 1 h reaction. Inset: The same data were mapped onto the 3D solution structure of the RRE RNA, for several catalysts and the control lacking a catalyst (red corresponds to highest reactivity; blue corresponds to reactivity below background).