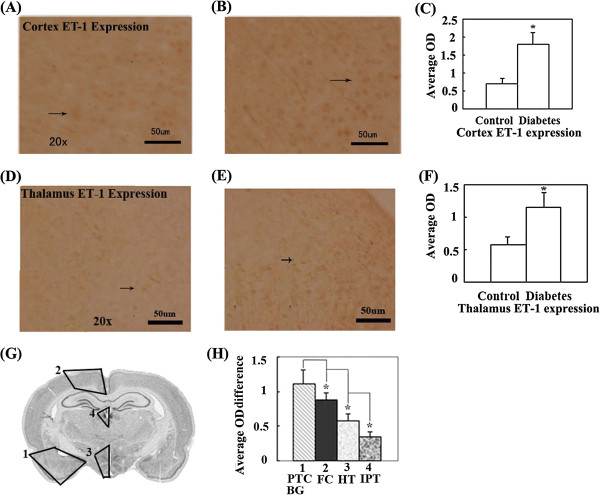
Figure 1.
ET-1 expression in distinct brain regions was compared by measuring the OD (Optic density) of positive cells in brains of control and diabetic rats with immunohistochemical staining. (A). The representative image of ET-1 expression in the cerebral cortex of control rats. (B). The representative image of ET-1 expression in the cerebral cortex of diabetic rats. (C). The OD comparison of ET-1 expression positive cells in cerebral cortex between control and diabetic rats. ET-1 expression in the cerebral cortex of diabetic rats significantly increases compared with control rats (*P < 0.05). (D). The representative image of ET-1 expression in the thalamus of control rats. (E). The representative image of ET-1 expression in the thalamus of diabetic rats. (F).The OD comparison of ET-1 expression positive cells in thalamus between control and diabetes rats. ET-1 expression in the thalamus of diabetes rats significantly increases compared with control rats (*P < 0.05). (G).Schematic representation indicates brain regions where ET-1 expression is significantly altered in diabetic rats and the rank order (from more to fewer) of expression quantity change in distinct regions of the integral brain. (H).The comparison of ET-1 expression quantity change in distinct brain regions. ET-1 expression quantity change is significantly different in distinct brain regions of diabetic rats (*P < 0.05). The black arrow indicates the positive cell. The marked number in distinct regions of the rat brain atlas reflects the rank order (from more to fewer) of expression quantity change in distinct regions of integral brain in all figures. Bar = 50 μm. Abbr. Basal ganglia, BG; Frontal cortex, FC; Hippocampus, HI; Hypothalamus, HT; Inferior part of thalamus, IPT; Partial frontal cortex, PFC; Partial temporal cortex, PTC; Temporal cortex, TC; Thalamus, TH.