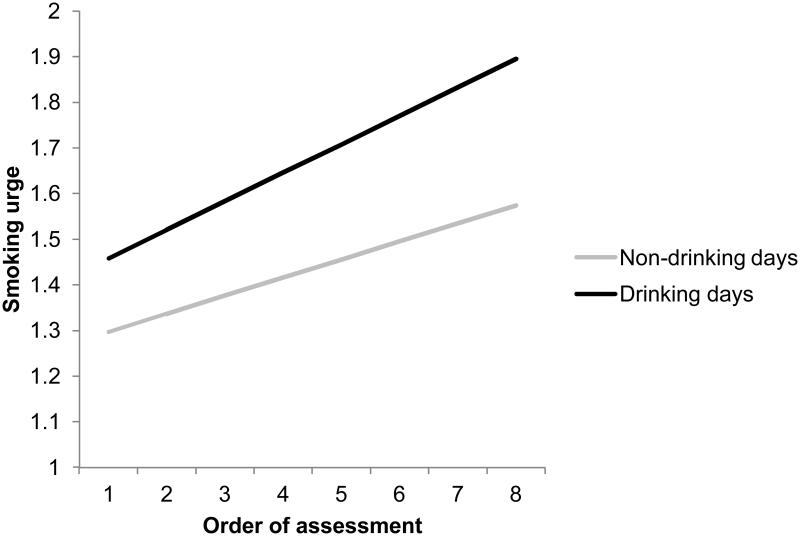
Figure 2.
Smoking urge intercept was higher on drinking days (simple intercept = 1.46) than on non-drinking days (simple intercept = 1.28). However, smoking urge trajectories were not different on drinking (simple slope = .062) and non-drinking days (simple slope = .039). Smoking urge was measured on a five point scale that ranged from “no urge” to “severe urge.” Order of assessment refers to the first through last assessment of a day.