Figure 2.
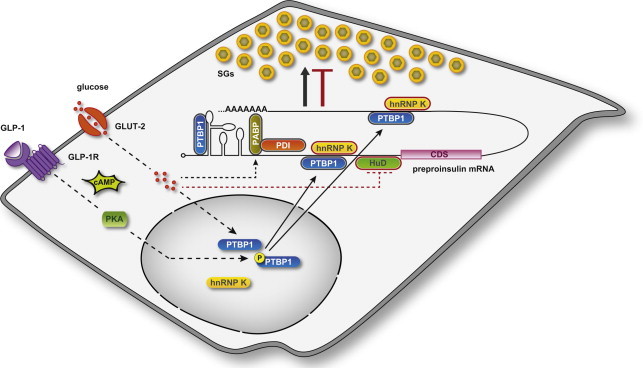
Model of RBP function in insulin expression and SG biosynthesis. Coordinated regulation by RBPs maintains insulin SG stores adequate to metabolic needs. Cytosolic RBPs with positive (PTBP1, PABP/PDI) and negative (HuD and hnRNP K) roles on insulin translation, and thereby SG biosynthesis, are outlined in black and red, respectively. Stimulation of β-cells induces cytoplasmic accumulation of PTBP1 through two distinct pathways. GLP-1 elevates intracellular cAMP levels, thereby activating PKA, which phosphorylates PTBP1 and thus prompts its redistribution into the cytoplasm. Glucose also triggers the cytosolic accumulation of PTBP1 through a phosphorylation-independent mechanism. In the cytoplasm PTBP1 binds to consensus sequences in the 5′- and 3′-UTRs of mRNAs encoding insulin and other proteins of the SGs. Glucose promotes the PABP-mediated binding of PDI to preproinsulin mRNA, whereas it inhibits that of HuD.
