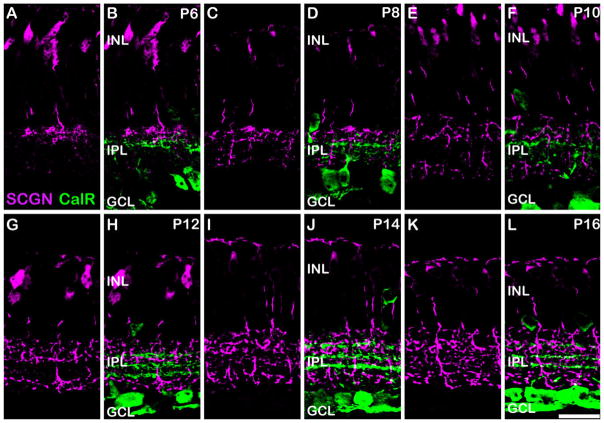
Figure 5.
Developmental expression of secretagogin in the mouse retina. Vertical sections from mouse retina aged postnatal day (P) 6–16, immunolabeled for secretagogin (magenta) and calretinin (CalR; green). A,B: P6. The central band of calretinin immunostaining is present and divides the ON and OFF sublaminae of the IPL. Most of the secretagogin stained bipolar cell axon terminals are located distal to the central band of calretinin staining suggesting their likely identity as OFF CBCs. C,D: P8. More secretagogin stained bipolar cell terminals are seen in the distal and proximal IPL. The density of bipolar cell terminals continues to increase at P10 (E–F) and P12 (G–H); however, the S3 region of the IPL remains relatively spared of secretagogin labeling. At P14 (I–J) and P16 (K–L), a higher number of axon terminals are seen in the S3 region of the IPL; however, the intensity of staining of these terminals appears to be comparatively weaker than the axon terminals in other strata. Scale bar = 20 μm.