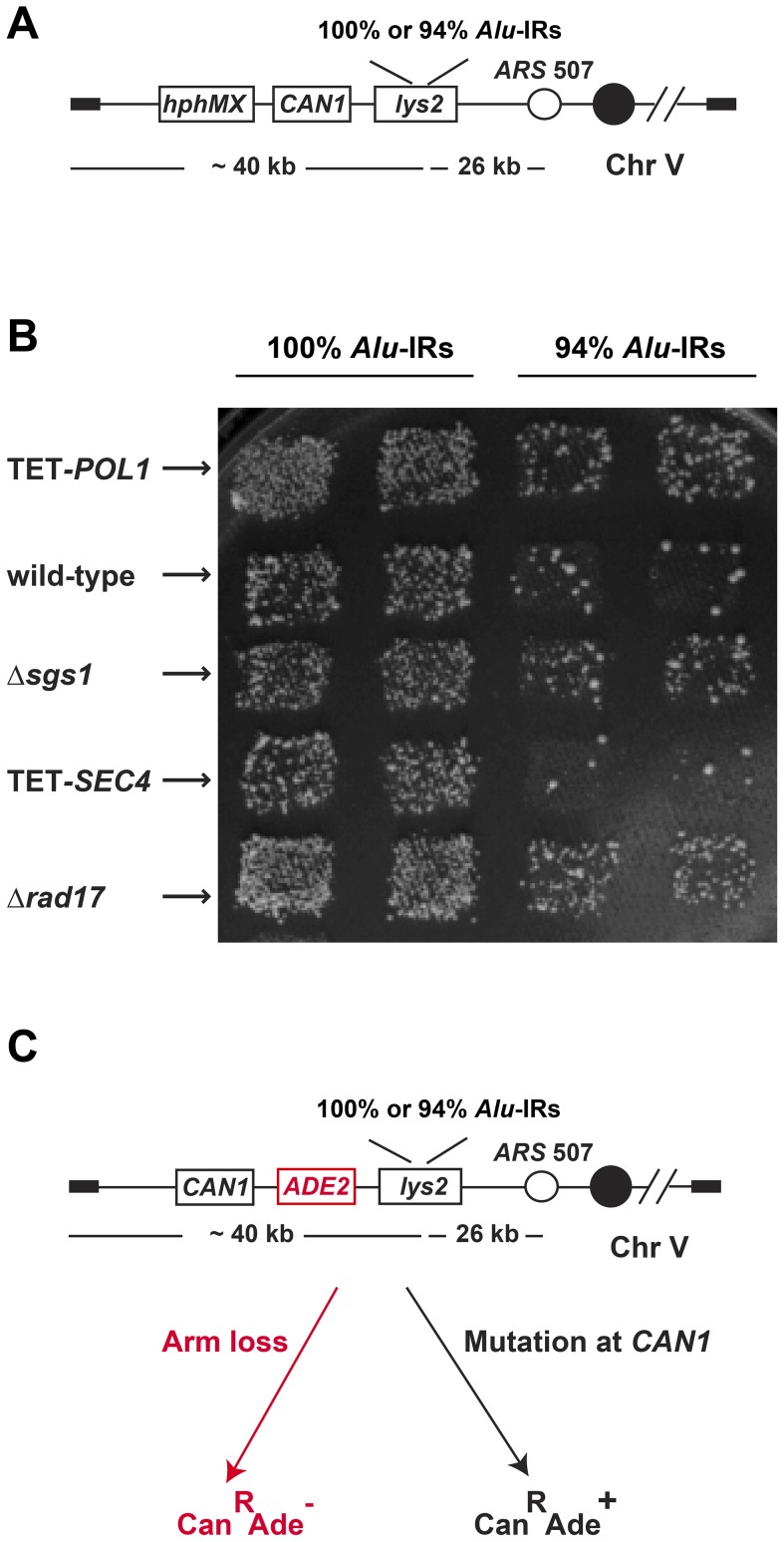
Figure 1. The genome-wide screen to identify hyper-GCR mutants.
(A) Experimental construct in the query strains. 100% homologous or 94% homeologous Alu-IRs were inserted into the left arm of chromosome V. The selectable marker hphMX for the presence of the chromosomal fragment containing the repeats and the counterselectable marker CAN1 used to assay GCR events are depicted. (B) Representative plate showing papillae on canavanine-containing medium reflecting the levels of Alu-IR-induced GCRs in wild-type and mutants. Columns are duplicates of query strains containing 100% homologous or 94% homeologous Alu-IRs. Each row is a tester strain containing the corresponding mutation. (C) Experimental construct for verifying the effect of hyper-GCR mutants obtained from the screen. ADE2 was inserted between CAN1 and the repeats. As a result, GCR events appear as red CanR colonies and mutations at CAN1 give rise to white CanR colonies on canavanine-containing medium with low amounts of adenine.