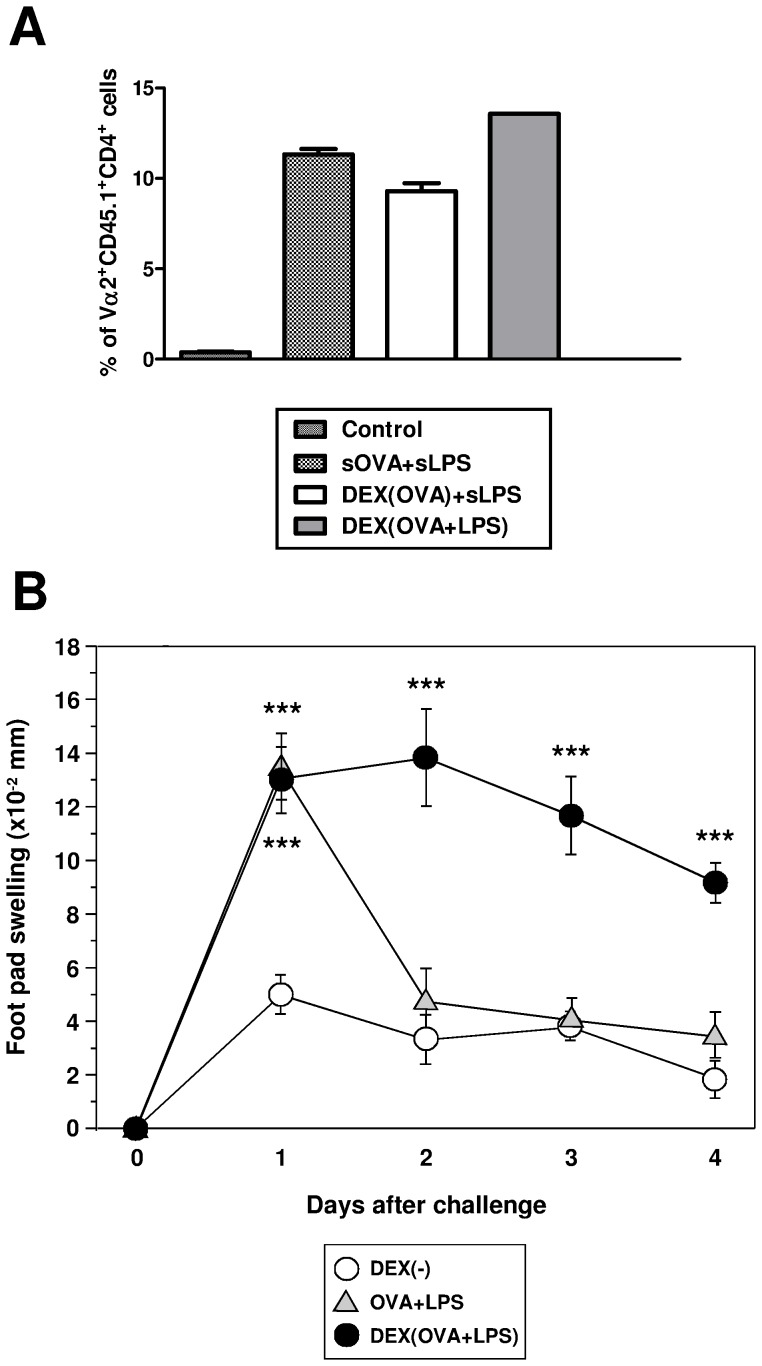
Figure 4. DEX particles containing OVA and LPS induce strong activation of CD4+ antigen-specific T cells when applied in vivo.
(A) Mice (C57BL/6) received CFSE-labeled OVA-specific OT-II T cells (107/mouse) i.v. Two days later, mice (three animals per group) were immunized i.v. with OVA (4 µg per mouse), LPS (0.4 µg), and DEX particles (each 200 µl) as indicated. After another three days, frequencies of CD4+CD45.1+Vα2+ OT-II T cells in spleen cell suspensions were analyzed by flow cytometry. Data represent mean±SEM of two independent experiments. The frequencies of proliferating CD4+ OT-II T cells in either treated group were signifiantly higher than in the non-immunized control group. (B) CD4+ DO11.10 T cells (5×106) were transferred to BALB/c mice (3 animals per group). One day later, OVA323–339 peptide (40 µg), LPS (100 ng), or different DEX particle formulations (each 40 µg) were injected as indicated. For challenge, LPS-stimulated BM-DCs were pulsed with OVA323–339 peptide (0.1 µg/ml), and were injected into either hind foot pad of pretreated BALB/c mice. Food pad thickness was recorded daily. Data represent mean±SEM of six recordings per group. Statistical significant differences between any group versus the control group (DEX[−]) are indicated (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).