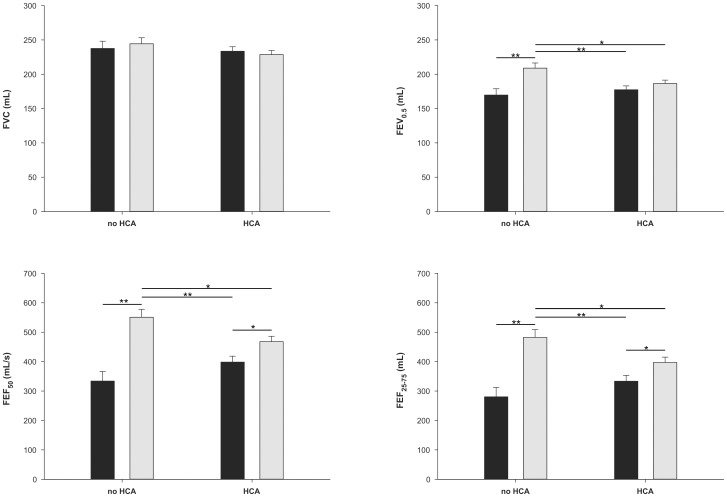
Figure 2. Lung function adjusted for body length and gestational age in male (black) and female (gray) premature infants.
Data are represented as the mean (+SD). Sixty-six (35 female) were exposed to HCA (combined Grade 1 and Grade 2) and 29 not exposed to HCA (17 female). There was a significant sex by HCA interaction for FEF50 (F = 8.76; p = 0.004), FEF25–75 (F = 8.11; p = 0.005) and FEV0.5 (F = 4.81; p = 0.031). Post hoc analyses revealed a significant reduction in lung function in exposed female preterm infants when compared to females not exposed to HCA. The effect of exposure to HCA was not significant in males. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (Post hoc Holm-Sidak test).