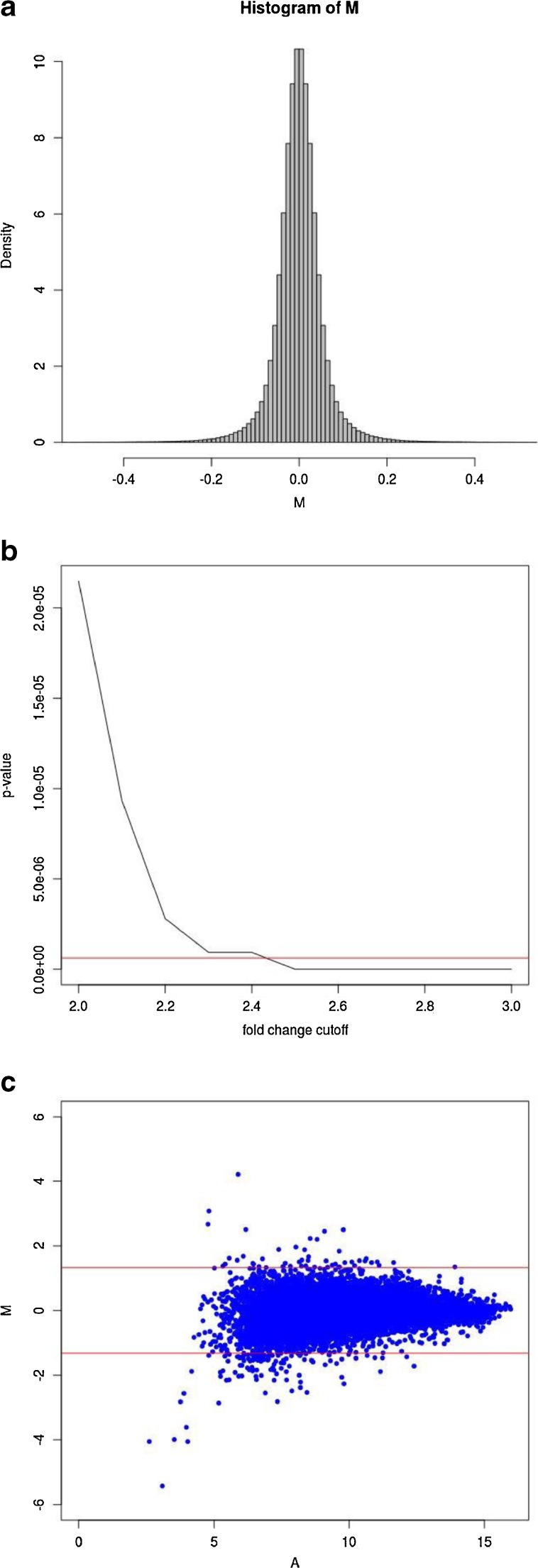
Fig. 1.
HTself2 analysis of microarray data. a. Self-self empirical probability density distribution. Virtual log ratios (M) where derived from all possible pairwise combinations among 6 independent wild type experiments analyzing gene expression in the ventral prostate at age 3 month. Fold-changes greater than 2-fold (M > 1 or M < −1) have a very small probability of happening (<0.0001) due by chance alone considering the intrinsic inter-animal genetic noise. b. Interchange between statistical significance and fold-chance cutoffs. Statistical significance thresholds (p-value) can be mapped directly to equivalent fold-change cutoffs to define differentially expressed genes in the knockout vs wild type experiment. The horizontal red line represents a traditional 0.01 significance cutoff after multiple testing correction by the stringent Bonferroni method. A 2.5-fold change cutoff criteria would be equivalent to a corrected p-value smaller than 0.01. c. MA-plot showing the knockout (KO) vs wild type (WT) experiment. Virtual log ratios (M) remain stable around zero (KO/WT = 1) along all average log intensity (A) scale. Horizontal red lines represent fold-change cutoffs (KO/WT > 2.5-fold or KO/WT < 1/2.5) presenting multiple testing adjusted p-values < 0.01 and, therefore, define the differentially expressed genes