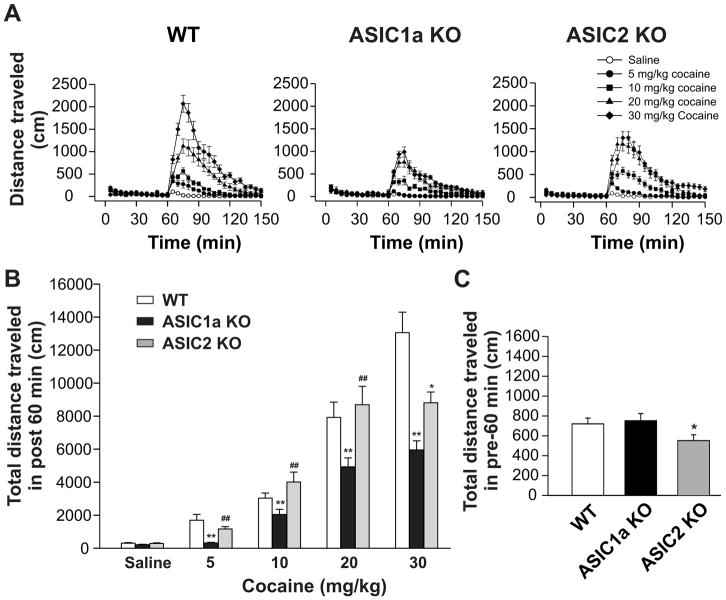
Fig. 3.
Effects of acute cocaine injection on locomotor activity in WT, ASIC1a−/−, and ASIC2−/− mice. Mice were placed in the locomotor test chamber for 180 min for accommodation purpose, with the final 60 min used as the control period. Either cocaine or saline were injected (i.p.) and mice were returned to their test chambers for an additional 90 min. (A) Time courses of locomotor activity of WT (left panel), ASIC1a−/− (middle panel), and ASIC2−/− (right panel) mice. Saline (open circles), 5 mg/kg (filled circles), 10 mg/kg (filled squares), 20 mg/kg (filled triangles) and 30 mg/kg (filled diamonds) doses of cocaine were given at the 60-min mark denoted on the graph. Initial 60 min (0 to 60 min) used as control period. Data shown are the average total distances traveled in 5-min intervals. n = 12 to 24 for each genotype. (B) Total distances traveled in 60 min immediately following injection of either saline or 5, 10, 20, or 30 mg/kg doses of cocaine in the three tested genotypes. Cocaine significantly increased locomotor activity in all genotypes of mice. n = 12 to 24 per each genotype. Data are means ± S.E.M. ANOVA was performed. Comparing WT and ASIC1a−/− mice, cocaine in all tested doses induced less locomotor activity in ASIC1a−/− mice compared to WT mice (** p < 0.01). Comparing WT and ASIC2−/− mice, cocaine at doses of 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg did not produce significant different locomotor activity in ASIC2−/− mice when compared with WT mice (p > 0.05). Cocaine at a dose of 30 mg/kg induced less locomotor activity in ASIC2−/− than in the WT mice (* p < 0.05). Comparing ASIC2a−/− and ASIC1a−/− mice, cocaine in all tested doses induced higher locomotor activity in ASIC2−/− mice compared to ASIC1a−/− mice (## p < 0.01). (C) Total distances traveled in 60 min for WT (n = 67), ASIC1a−/− (n = 71), and ASIC2−/− (n = 66) mice during their habituation to the chambers immediately prior to cocaine or saline injection. No significant differences existed between WT and ASIC1a−/− mice (p > 0.05). ASIC2−/− mice displayed decreased locomotor activity when compared to WT or ASIC1a−/− mice (*p < 0.05). Data are means ± S.E.M. WT: wild-type mice; ASIC1a KO: ASIC1a knockout mice; ASIC2 KO: ASIC2 knockout mice. Min: minutes.