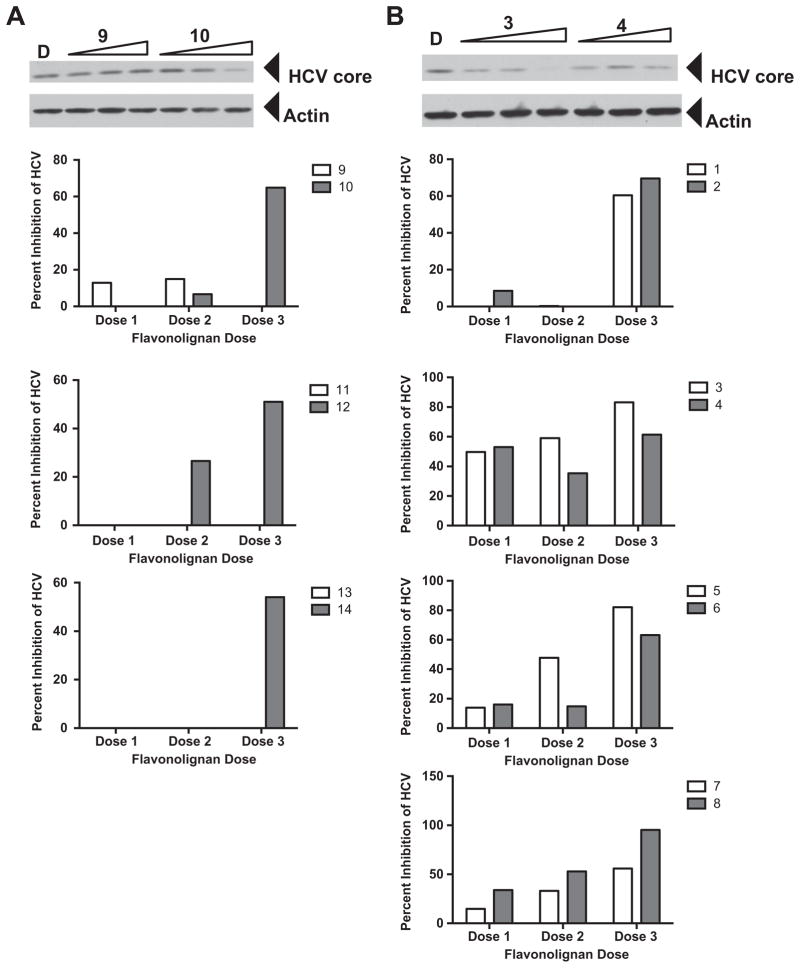
Figure 2.
Antiviral profile of parent and 7-O-methyl flavonolignans. Huh7.5.1 cells were infected with JFH-1 at a multiplicity of infection of 0.05. Virus inoculum was removed after 5 h and compounds were added. Cultures were incubated for 72 h before protein lysates were analyzed for HCV core protein expression by Western blot analysis. Detection of actin protein served as a protein loading control. Panel A depicts an example of a parent compound that lacked anti-HCV activity (9) and acquired anti-HCV activity upon methylation (10). Panel B depicts an example of a parent compound that had anti-HCV activity (3) and decreased anti-HCV activity upon methylation (4). The graphs below panels A and B present quantitation of HCV core pixel intensity following normalization to actin pixel intensity, expressed as percent inhibition relative to DMSO controls. Graphs below panel A depict parent compounds that lacked anti-HCV activity (9, 11, 13) and acquired anti-HCV activity upon methylation (10, 12, 14). Graphs below panel B depict parent compounds that had anti-HCV activity (1, 3, 5, 7), and retained (2), decreased (4, 6), or enhanced (8) anti-HCV activity upon methylation. Doses used were derived from toxicity data, such that two non-toxic concentrations and one near the IC50 value were evaluated in the antiviral assay. Concentrations for compounds 1, 3, and 5: 6.2, 20.7, 62.1 μM. Concentrations for compounds 2, 4, 6, and 14: 0.8, 2.7, 8.0 μM. Concentrations for compounds 7 and 8: 1.6, 5.4, 16.1 μM. Concentrations for compounds 9, 11, 12 and 13 12.4, 41.4, 124.2 μM. Concentrations for compound 10: 6.0, 20.1, 60.3 μM.