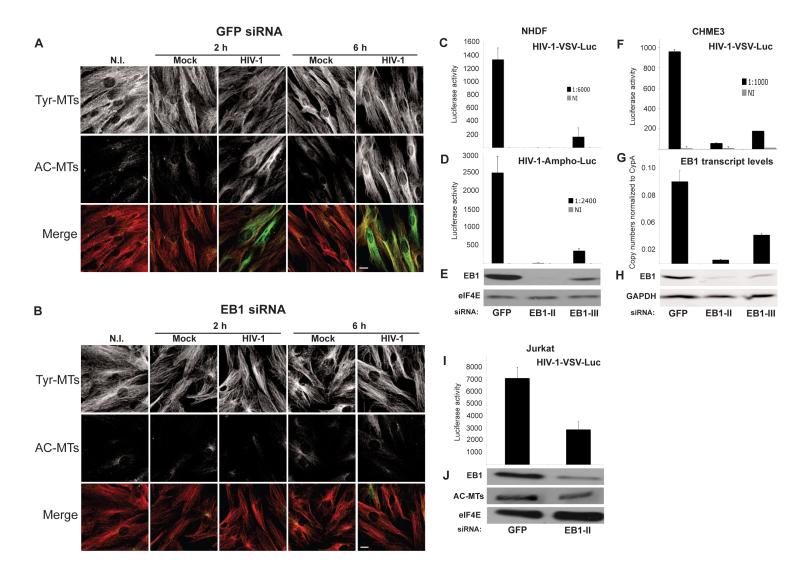
Figure 4. EB1 is required for HIV-1 mediated MT stabilization and infection.
(A-B) NHDFs were transfected with control GFP siRNA (A) or EB1 siRNA (B) and then non-infected (N.I.), mock infected or infected with HIV-1-VSV at m.o.i. 3. Samples were fixed at the indicated h.p.i. and stained for Tyr-MTs and AC-MTs. Images are shown for representative fields. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C-E) NHDFs were transfected with control GFP siRNA or two independent EB1 siRNAs (EB1-II and EB1-III) and then infected with HIV-1-VSV-Luc (C) or HIV-1-Ampho-Luc (D). Levels of infection were determined by luciferase assay. (E) WB analysis demonstrated the extent of EB1 depletion in samples. eIF4E served as a loading control. (F-H) CHME3 cells were transfected with control, EB1-II or EB1-III siRNAs and then infected with HIV-1-VSV-Luc. (F) Luciferase assays were used to determine levels of infection. (G) qPCR showing EB1 transcript levels in each sample. (H) WB analysis of EB1 depletion in samples. GAPDH served as a loading control. (I-J) Jurkat cells were treated with control or EB1-II siRNAs and infected with HIV-1-VSV-Luc. (I) Luciferase assays were used to determine levels of infection. (J) WB analysis of EB1 depletion and AC-MTs in samples. eIF4E was used as loading control. Data in C, D, F, G and I are represented as mean +/− SEM. See also Figure S2.