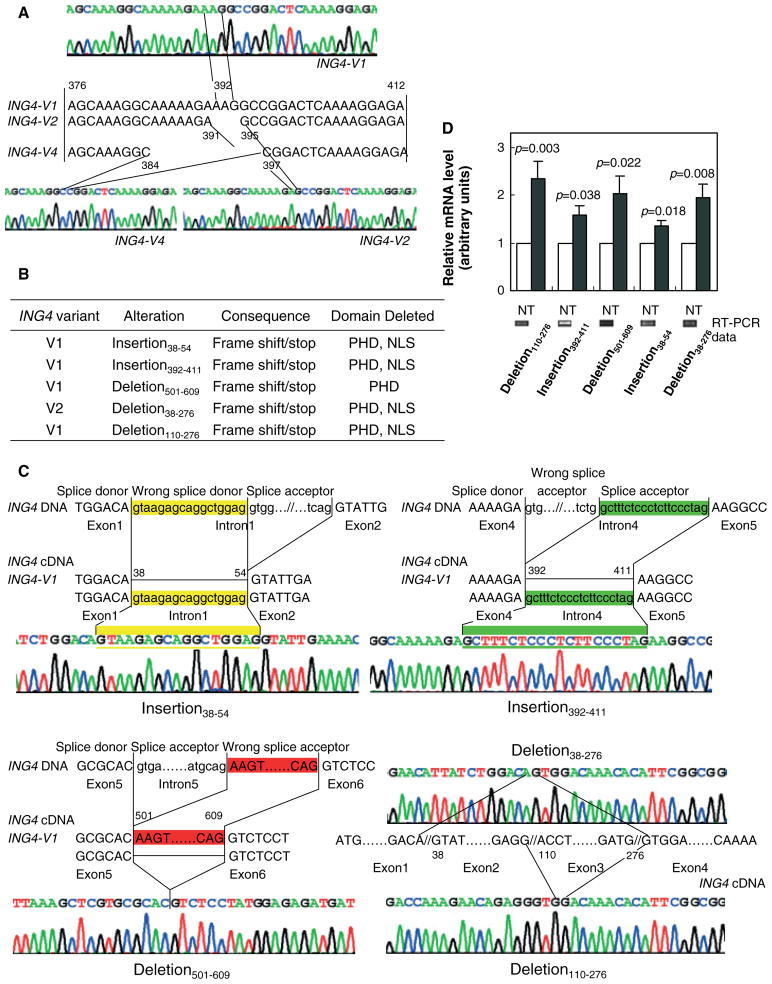
Figure 3.
Five novel aberrantly spliced variant forms of ING4 v1 and ING4 v2 were found in gastric adenocarcinoma tissues. (A) ING4 v1, ING4 v2, and ING4 v4 (but not ING4 v3) were detected in stomach adenocarcinoma cell lines and tissues. The partial sequence maps of ING4 v1, v2 and v4, and cDNA sequences of the variable region (exon 4) of the three ING4-spliced variants are shown. (B) List of the five novel ING4 v1 and ING4 v2 insertions and/or deletions. PHD and NLS stand for the c-terminal plant homeo-domain zinc-finger domain and the bipartite nuclear localization signal domain, respectively. (C) Schematic representations of 38–54 (yellow; upper left panel) and 392–411 (green; upper right panel) insertions, and 501–609 (red; lower left panel) deletion in ING4 v1. Upper- and lowercase letters represent exon and intron sequences of ING4 genomic DNA, respectively. Splice donor, wrong splice donor causing the alteration, and splice acceptor are noted. ING4 v1 and ING4 v2 sequences are also shown. Schematic representations of deletion (38–276) of ING4 v2 and deletion (110–276) of ING4 v1 (lower right panel). Sequence maps of ING4 exons 1, 2, 3, and 4 indicate that stomach adenocarcinoma tissues harbour deletion of nucleotides 38–276 which include the second exon and the third exon of ING4 v2, and deletion of nucleotides 110–276 which include the third exon of ING4 v1 in the stomach adenocarcinoma cell line MGC-803. (D) The mRNA levels of the ING4 variants in normal (N) and tumour (T) tissues. Deletion 110–276 (T, n = 15; N, n = 13). Insertion 392–411 (T, n = 8; N, n = 11). Deletion 501–609 (T, n = 12; N, n = 11). Insertion 38–54(N, n = 7; N, n = 7). Deletion 38–276 (N, n = 10; T, n = 9). The values for normal tissues were normalized to 1. Representative RT-PCR gels for normal tissues are also shown