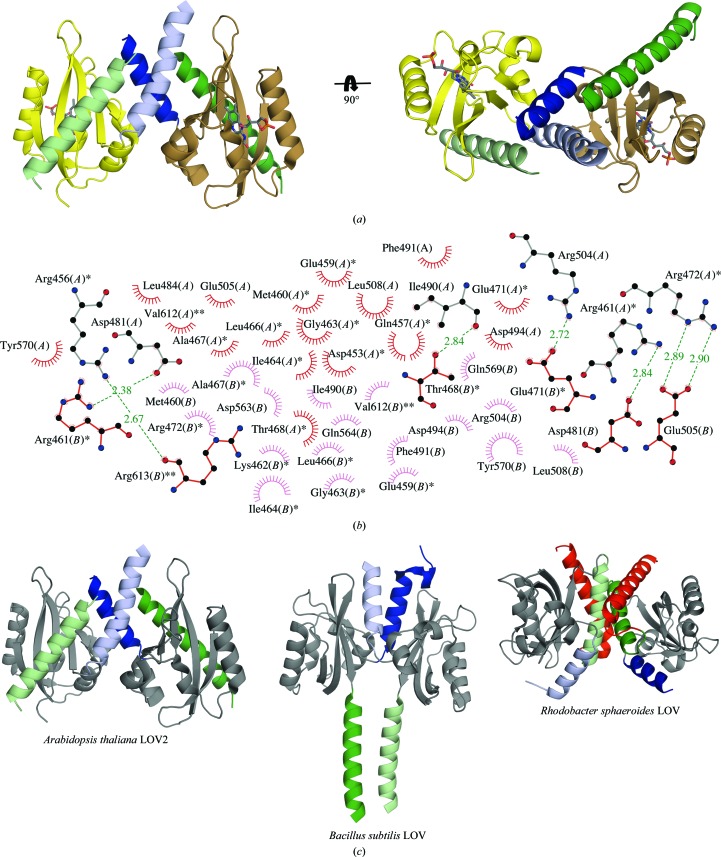
Figure 2.
Dimerization of AtLOV2. (a) AtLOV2 dimer in which the flanking linker helices form an α-helical coiled coil. (b) Dimerization interface of AtLOV2. Residues with one star belong to the A′α helix and those with two stars belong to the Jα helix; unlabeled residues are from the PAS core domain. (c) Varied dimerization modes of AtLOV2, Rhodobacter sphaeroides LOV (RsLOV; PDB entry 4hj4; Conrad et al., 2013 ▶) and the Bacillus subtilis LOV domain of FixL (PDB entry 4gcz; the histidine kinase domain of the chimera was omitted for clarity; Diensthuber et al., 2013 ▶). The A′α helix is colored light blue (chains A) and dark blue (chains B) and the Jα helix is depicted in light green (chains A) and dark green (chains B). The LOV core domains of the displayed structures are shown in gray. The Kα helix C-terminal to the Jα helix is shown in red for both chains in the RsLOV structure.