Fig. 1.
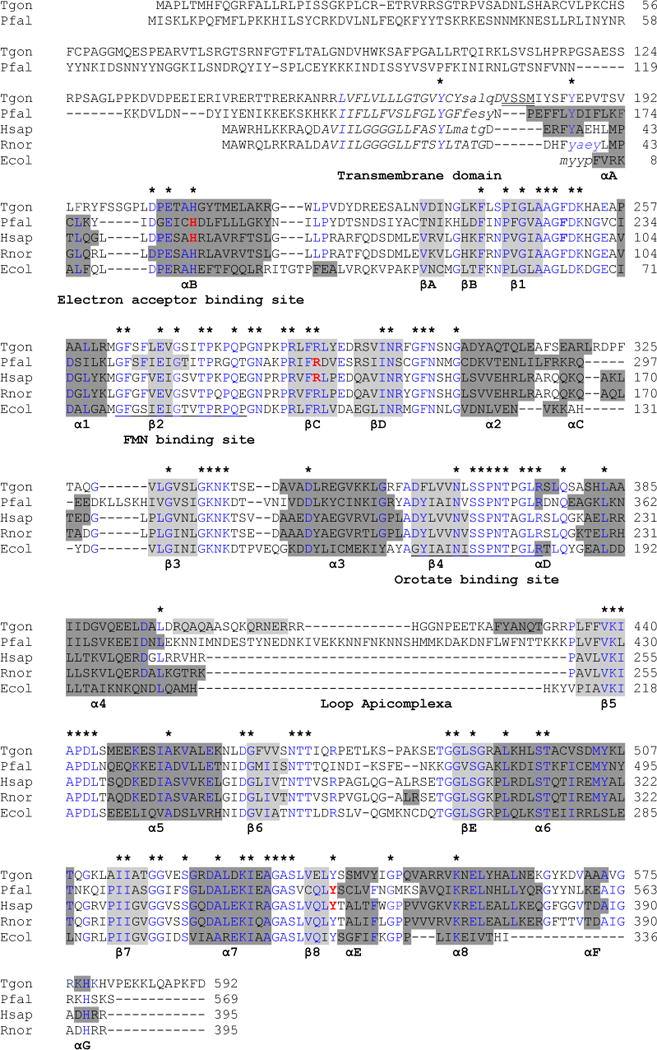
Alignment of the T gondii DHOD predicted amino acid sequence with other family 2 DHODs. Alignment of the T gondii DHOD predicted amino acid sequence with other family 2 DHODs based on [27]. Secondary structural representation of the DHOD motifs from the PDB-viewer; alpha helices show in dark gray and beta sheets in light gray. The N-termini of the predicted 3D structure for TgDHOD and for the crystallographic structures (1TV5, 1D3G, 1UUO and 1F76) are shown in lowercase. In the central barrel α-helices are named α1–α8, and β-sheets are named β1–β8. Alpha-helices and β-sheets outside the barrel are named αA–αG and βA–βE as in [27]. Partially conserved amino acids within the sequences are shown in blue and completely conserved residues are indicated above the alignment with asterisks. The N-terminal transmembrane domains predicted by HMMTOP are shown in italics. The first four residues of the recombinant protein described in the present report are indicated with double underlining. FMN and orotate binding site described in [76] are underlined. Amino acids interacting with A77-1726 are in red and bold (PfDHOD: H185, R265, Y528 [31], HsDHOD: H55, R135, Y355 [29]).
