Fig. 2.
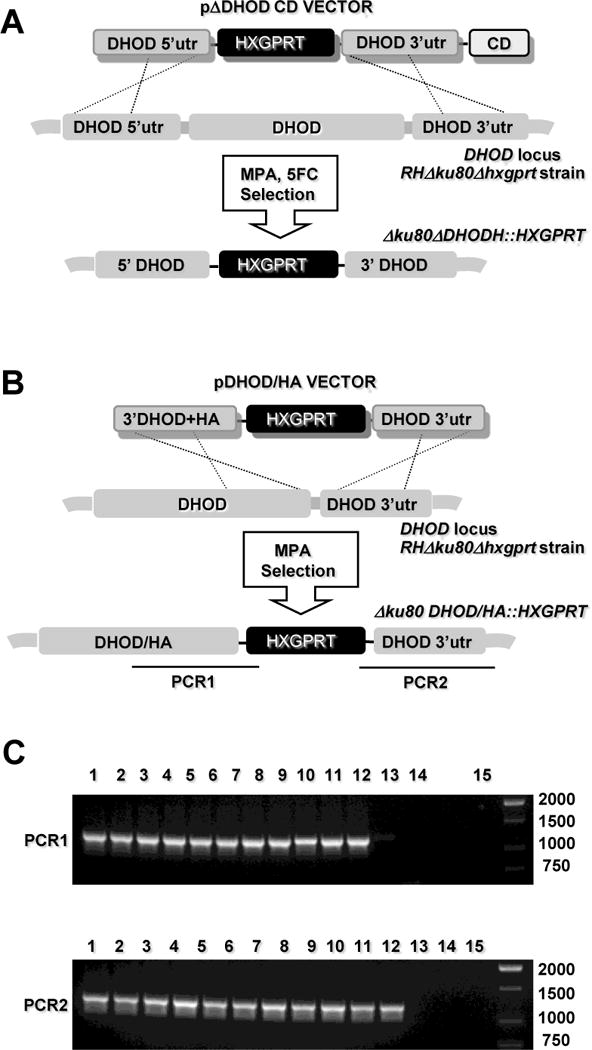
Targeted deletion or insertion at the DHOD gene. (A) Strategy for disrupting the DHOD gene via integration of the HXGPRT marker. Targeting plasmid pΔDHOD and pΔDHODCD targets a ~ 10 kb deletion of the DHOD coding region (see Materials and Methods). Parasites were first selected by positive selection for HXGPRT in MPA + xanthine, then later by negative selection against the downstream cytosine deaminase (CD) marker in MPA + xanthine + 5-fluorocytosine (5FC) to enrich for clones lacking inserting of the CD gene. (B) Strategy for HA tagging the C-terminus of DHOD and inserting the (2 kb) HXGPRT selectable marker immediately following the termination codon of DHOD. (C) Genotype validation of MPA resistant clones selected following transfection with plasmid pDHOD/HA. Top gel panel (PCR 1): selected MPA resistant clones (lanes 1 – 12); parental RHΔku80Δhxgprt (lane 13), RH (lane 14), DNA size ladder (lane 15). PCR 1 produces a 1,219 bp product from a correctly targeted clone (lanes 1 – 11), but not from the parent strains. Bottom gel panel (PCR 2): selected MPA resistant clones (lanes 1 – 12); parental RHΔku80Δhxgprt (lane 13), RH (lane 14), DNA size ladder (lane 15). PCR 2 produces a 1,259 bp product from a correctly targeted clone (lanes 1 – 11), but not from the parent strains.
