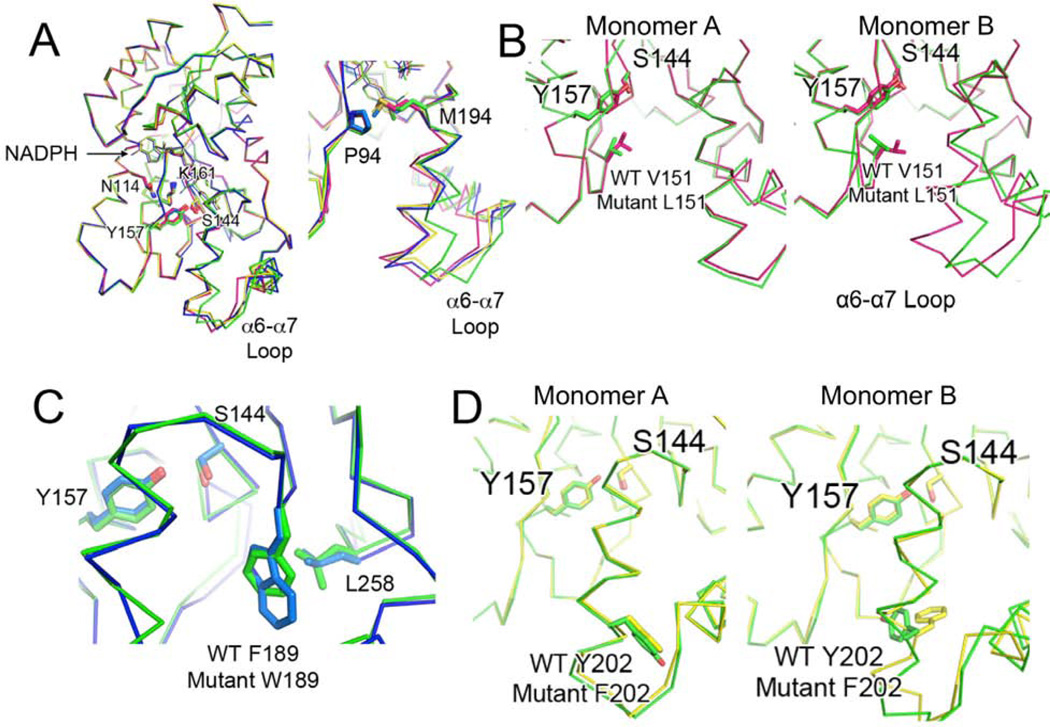
Figure 4. see also Figure S2 Mutant ActKR Structural Analysis.
(A) (Left) Alignment of monomer B of V151L (magenta), F189W (blue), and Y202F (yellow) to that of wild-type actKR (green). Although the catalytic residues and NADPH cofactors align well, the mutant monomers are in a closed conformation relative to wild-type, as seen by the shifts in the labeled α6-α7 loops and extended M194 side-chains (right).
(B) Residue 151 extends into the substrate pocket similarly in monomer A of wild-type (green) and V151L (magenta) (left), but L151 in the mutant monomer B points more toward the α6-α7 loop, creating a smaller substrate pocket (right)
(C) The aromatic plane of W189 in the F189W mutant (blue) coincides with that of wild-type F189 (green). L258 may hydrophobically interact with W189, limiting the substrate pocket size.
(D) Residue 202 overlaps when monomer A of wild-type (green) and Y202F (yellow) are aligned (left), but in monomer B (right), the wild-type Y202 points away from the substrate pocket while the mutant F202 points within the pocket.