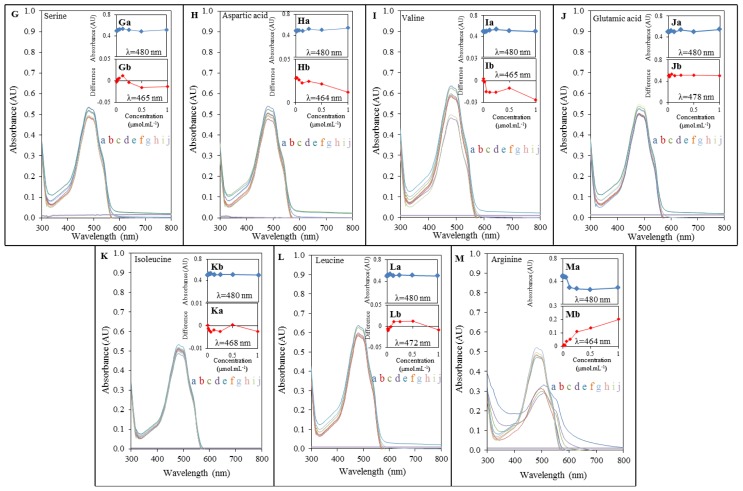
Figure 3.
Interactions of amino acids (1; 2; 3; 6; 12; 25; 50; 100 μmol mL−1) with doxorubicin (100 μg mL−1) monitored with spectrophotometry. DOX interaction with: (G) serine; (H) aspartic acid; (I) valine; (J) glutamic acid; (K) isoleucine; (L) leucine; (M) arginine, where (a) stays for 100 μmol mL−1; (b) for 50 μmol mL−1; (c) 25 μmol mL−1; (d) 12 μmol mL−1; (e) 6 μmol mL−1; (f) 3 μmol mL−1; (g) 2 μmol mL−1; (h) 1 μmol mL−1; (i) 0 μmol mL−1 and (j) for control (AA without DOX). The dependence of the absorbance at 480 nm on the different concentrations of amino acids can be observed in insets marked with lowercase letter a. Insets marked with lowercase letter b express the differences obtained from differential spectra gained as readout of DOX spectrum from DOX-AA complex spectrum with observed wavelength changes.