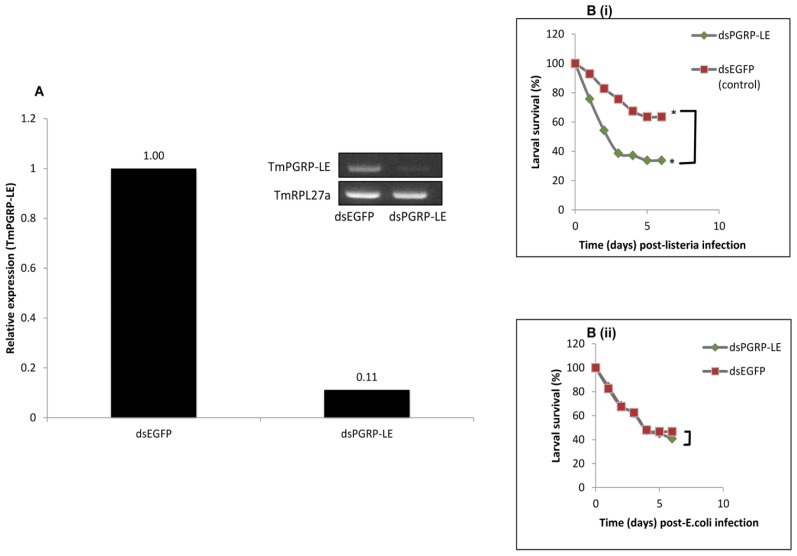
Figure 5.
Effect of TmPGRP-LE knockdown on the survivability of T. molitor larvae (A) Silencing of TmPGRP-LE mRNA in the larvae of T. molitor by RNA interference. Real time qRT-PCR and semi-quantitative PCR methods were used to study the gene knockdown levels in the group injected with dsPGRP-LE prior to immune challenge by Listeria. The control group was injected with dsEGFP. A housekeeping gene TmRPL27a was used as an internal control during PCR reactions; (B) Survival pattern of T. molitor larvae following immune challenge by L. monocytogenes. Larvae whose gene expression was down regulated by RNAi exhibited a significant (p < 0.05) (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test) reduction in survivability as compared to the control group “*” represent a statistically significant difference between means (B-i); Replacing L. monocytogenes with E. coli did not result in the differential survival pattern observed with the intracellular pathogen L. monocytogenes (B-ii). Results presented here are an average of three independent biological replicate experiments.