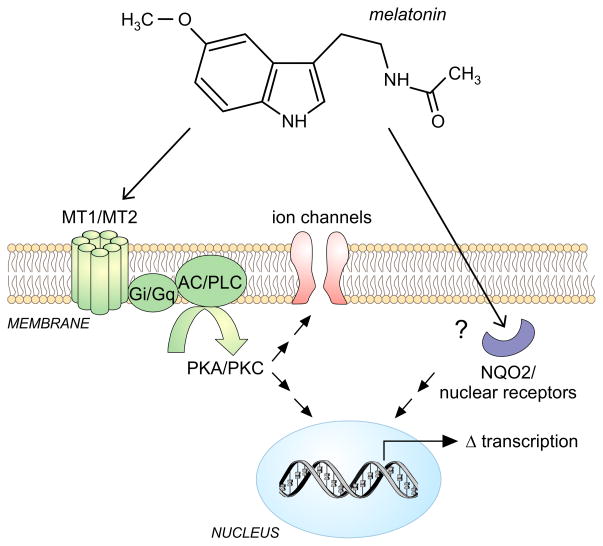
Figure 2.
Melatonin signaling and modulation of the molecular clock. Melatonin is the most-studied pharmacological agent that modulates and benefits the circadian system. Melatonin interactions with the MT1 and MT2 G-αi and G-αq protein coupled receptors lead to the inhibition of adenylate cyclase (AC) and Phospholipase C (PLC) and down regulation of PKA/PKC signaling altering ion channel function and changes in circadian-related transcription. Melatonin also binds the enzyme quinone reductase 2 (NQO2) and modulates the function of nuclear receptors although the physiological significance of this binding is not yet clear.