Figure 3. Adult-onset Muscle Mitochondrial Perturbation Increases Lifespan and Preserves Mitochondrial and Muscle Function.
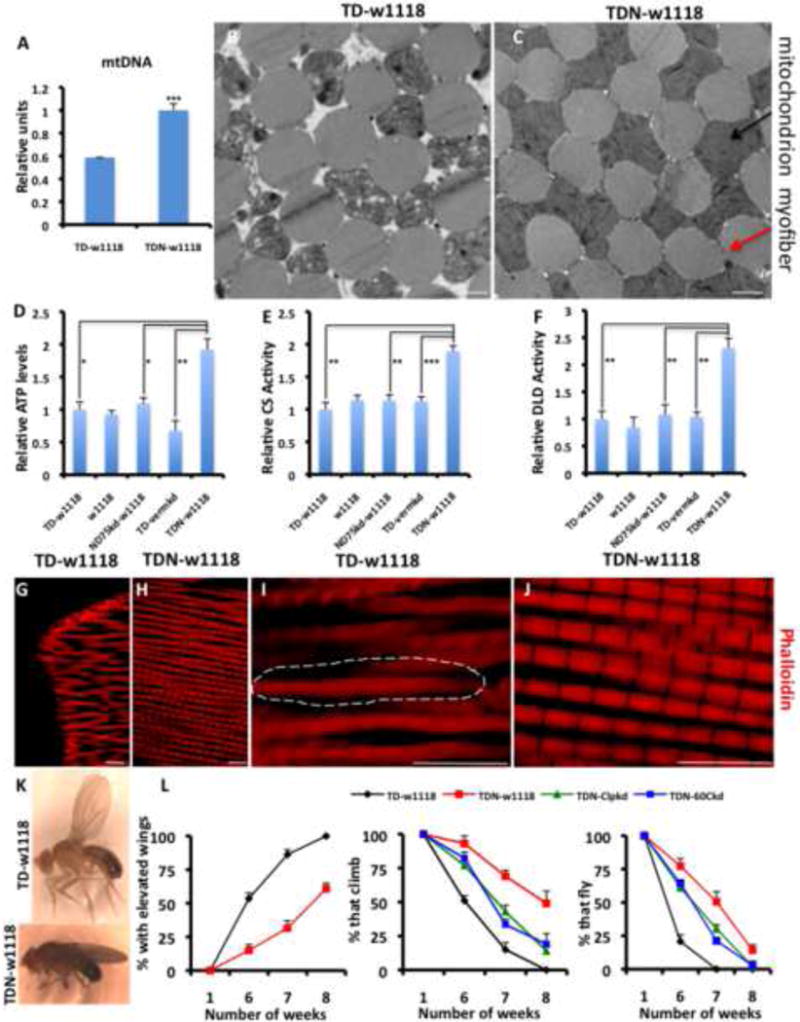
(A) Mitochondrial mass assessed as relative mitochondrial DNA levels, is higher in TDN muscles relative to TD. n=4.
(B and C) TEMs of TD (B) and TDN (C) muscles. Note the large interstitial spaces between remnants of degenerating mitochondria (black arrow) and myofibrils (red arrow) in the TD muscles. Scale bar is 1.0μm
(D-F) Relative ATP levels (D), Citrate Synthase (CS) activity levels (E), and Dihydrolipoamide Dehydrogenase (DLD) activity levels (F). Figure labeling is as follows: (i) tub-Gal80ts;Dmef2-Gal4 crossed to w1118 labeled as TD-w1118 (negative control), (ii) w1118 (i.e as wildtype flies), (iii) The ND75RNAi-weak line crossed to w1118 labeled as ND75kd-w1118 (control for insertion site), (iv) tub-Gal80ts;Dmef2-Gal4 crossed to a vermillionRNAi line labeled as TD-vermkd (RNAi negative control), and (v) tub-Gal80ts,ND75RNAi-weak;Dmef2-Gal4 crossed to w1118 labeled as TDN-w1118. n=4.
(G-J) Indirect Flight Muscles of seven-week old TD (G and I) and TDN (H and J) flies stained with phalloidin (red) to mark the sarcomeres. (I and J) are higher magnifications of (G and H), respectively (see scale bars). Note the severely disorganized sarcomere structure of TD flight muscles; the broken lines surround an area where the sarcomeres are indistinct, in contrast to the well-arranged sarcomeres of TDN flies. In addition, TD myofibers were frequently found to be transected, as shown in G. Scale bar is 10.0μm
(K) An example of a TD fly with elevated wings (top) compared to a TDN fly (lower panel).
(L) In all panels, TD flies are shown in black, TDN in red, TDN with ClpX knockdown, green, and TDN with Hsp60C knockdown is shown in blue. Left panel; most TD flies have elevated wings relative to TDN flies. Middle panel; climbing ability is preserved in TDN flies as they age, compared to TD flies. Knockdown of ClpX or Hsp60C suppresses the enhanced climbing ability. Far right panel shows the flight ability of the flies, which is preserved in TDN flies. n=4 independent cohorts with the starting number of flies for each genotype in each cohort = 100, p<0.001 for all comparisons between TD and TDN at 6, 7 and 8 weeks.
Error bars denote s.e.m; and * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.01 and *** = p<0.001. Also see Figures S3-S5 and Tables S3-S5.
