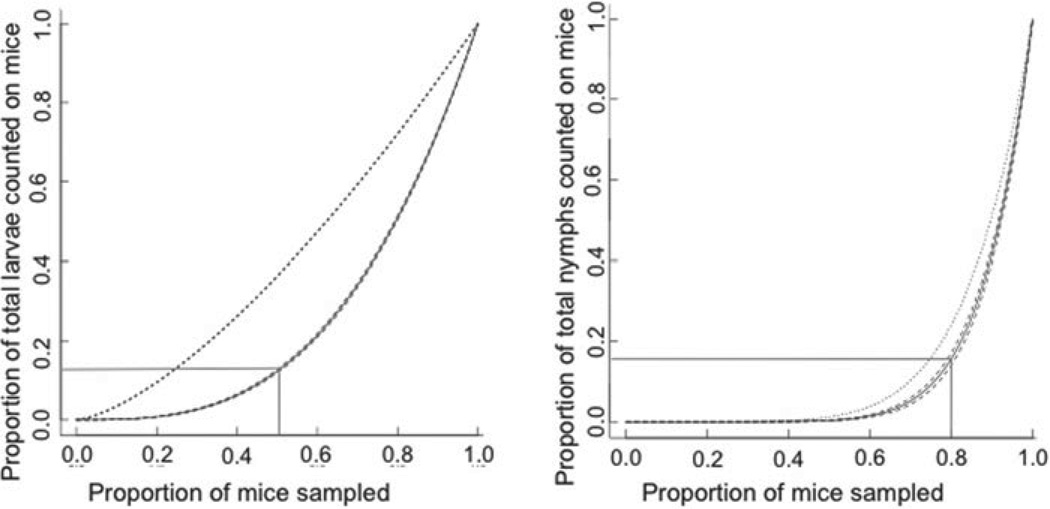
Fig. 2.
The majority of ticks parasitized a minority of mice. Data are plotted as the cumulative frequency distribution of attached larvae (A) and attached nymphs (B) on mice that are ranked from lowest to highest burden. The black curve represents the model that best explains the distribution of tick burdens on mice from all trapping sessions surrounded by the 95% confidence interval for this model (dashed curves). The dotted line represents the cumulative distribution of ticks on mice assuming ticks are randomly distributed among mice. The grey lines demonstrate that half of the mice host only 16% of the larvae, while the remaining mice host 84% of attached larvae. Similarly, 80% of the mice host only 17% of all attached nymphs while the remaining 20% of the mice host 83% of the nymphs.