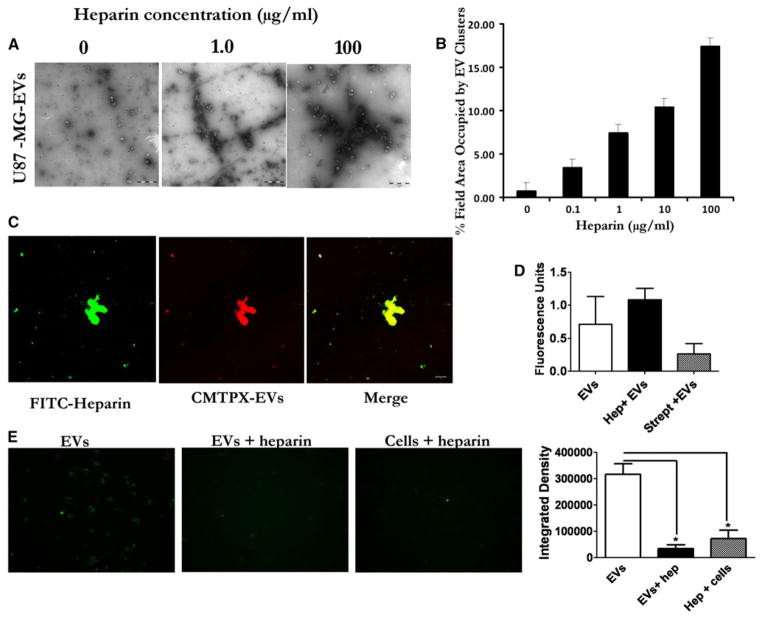
Fig. 2.
Heparin causes EV aggregation and binds EVs. a Suspensions of EVs derived from U87-MG cells in PBS were incubated with 0–100 μg/ml of heparin for 30 min at RT and then imaged by transmission EM (TEM). Scale bar = 1 μm. b Quantification of the TEM images show increased area occupied by the EV clusters as heparin concentration increases. (C) Confocal imaging of complexed FITC-heparin (green) and U87-MG -derived EVs (CMTPX-red). Merging of the images of FITC-heparin and EVs shows colocalization of heparin and EVs in yellow (Scale bar = 10 μm). d Incubating heparin with EVs increases their pelleting efficiency. PKH67 labeled U87 EVs were mixed with PBS, heparin, or streptavidin and pelleted 2 h at 100,000×g. Pelleted EVs were resuspended and fluorescence activity measured using a plate reader. e Binding heparin to cells reduces EV uptake. U87 glioma cells were incubated on ice with PBS or heparin (200 μg/ml) before adding PKH67 labeled U87-derived EVs. For control we incubated heparin and EVs at room temperature (EVs + heparin) before adding to cells. Magnification × 20