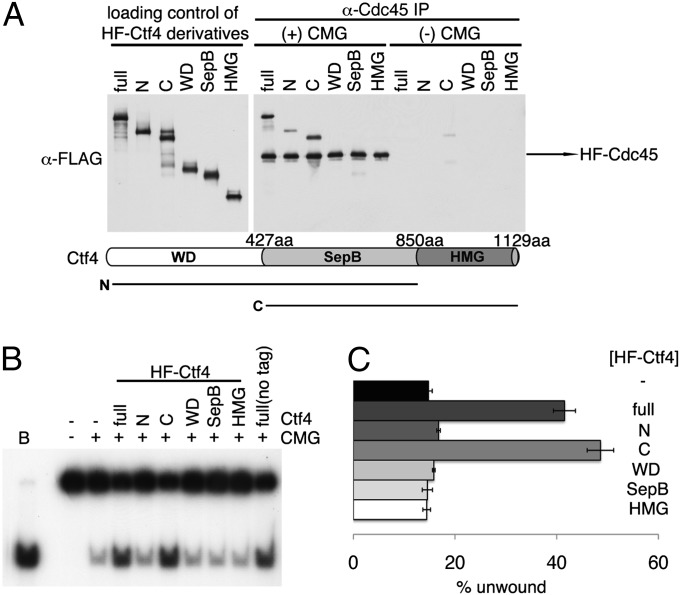
Fig. 4.
Physical and biochemical interactions between different domains of hCtf4 and the hCMG complex. (A) Various derivatives of HF-hCtf4 [300 fmol of full-length, N (WD + SepB), C (SepB + HMG), and SepB domains, which are likely to be dimers, and 600 fmol of WD and HMG domain, which are likely to be monomers] were incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the hCMG complex (100 fmol). Mixtures were then immunoprecipitated with 1 μg of α-Cdc45 antibodies. Loading controls and immunoprecipitated materials were gel-separated and then analyzed by Western blotting against the FLAG tag to detect HF-hCtf4 derivatives and HF-hCdc45. The domains of hCtf4 are shown below the gel. (B) HF-hCtf4 derivatives (50 fmol as dimers and 100 fmol of monomers) used in A and the hCMG complex (100 fmol) were mixed and incubated in standard helicase reaction mixtures containing 50 mM NaCl. Untagged, full-length hCtf4 was also included as a control (last lane). (C) Unwound substrate (%), presented in B, was calculated and is shown in the graph.