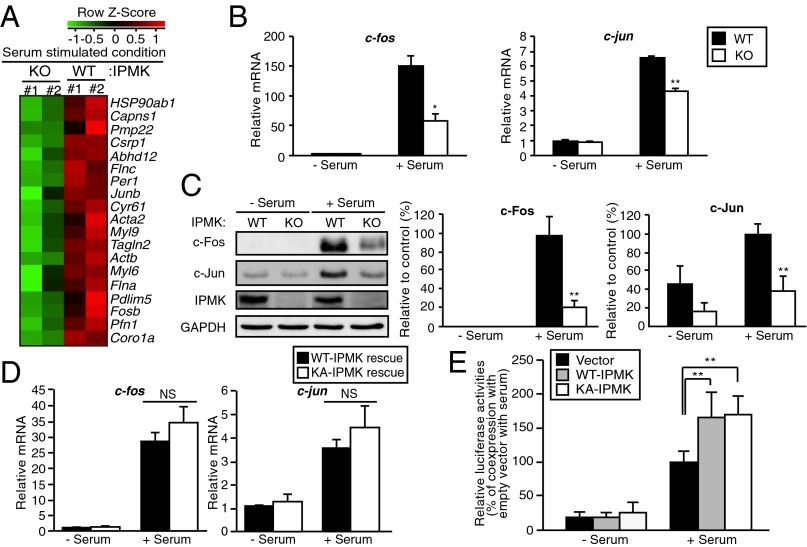
Fig. 1.
IPMK promotes SRF-induced gene activation. (A) Microarray analysis of gene expression profiles in serum-stimulated wild-type (WT) and IPMK-deleted (KO) MEFs. Cells were deprived of serum for 12 h and stimulated with 10% FBS for 30 min. Major serum-inducible SRF target genes were clustered. Increased and decreased gene expression labeled in red and green, respectively. (B) The mRNA levels of the SRF target genes c-jun and c-fos as measured via qPCR. Cells were deprived of serum for 12 h and stimulated with 10% FBS for 30 min. (C) Immunoblot analysis of protein levels. Proteins were prepared from WT and IPMK-deleted MEFs that were stimulated with 10% FBS for 1 h. (D) Proteins were isolated from IPMK-deleted MEFs stably expressing wild-type (WT) or the catalytically inactive, mutant K129A IPMK (KA), followed by immunoblotting. (E) SRE reporter activity along with empty vector, WT-IPMK, or catalytically inactive, mutant K129A IPMK (KA) expression plasmids in transiently transfected HEK293 cells. At 36 h posttransfection, cells were incubated in serum-free DMEM overnight followed by 10% FBS treatment for 6 h. Constitutively expressing Renilla luciferase was used as an internal control for normalizing transfection efficiency. The results are presented as relative luciferase activities compared with the activity after coexpression of empty vector in serum-treated condition, which was set as 100%. Bars represent mean ± SE (B and D) or ± SD (C and E) (n = 3–5). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS, not significant.