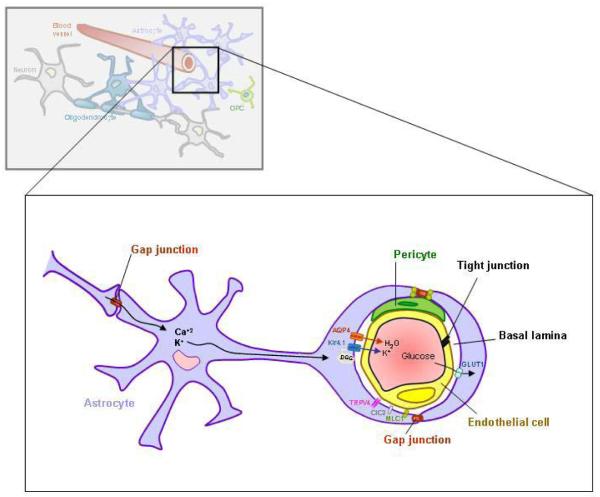
Figure 2. Astrocytes and the blood brain barrier.
The blood brain barrier (BBB) structure relies on the properties of endothelial cells of brain capillaries which are sealed by tight junctions and surrounded by basal lamina, pericytes and astrocyte endfeet. The water channel aquaporin-4 (AQP4) and the potassium channel Kir4.1 involved in water and potassium exchange are enriched in the membranes of astrocytic endfeet where they are stabilized by the association with the dystrophin-dystroglycan associated complex (DGC). At this site astrocyte endfeet are highly enriched in ion channels among which the chloride channel ClC2, the calcium channel TRPV4 and the putative ion channel MLC1. Uptake of glucose from the blood circulation by astrocytes occurs via the glucose transporter-1 (GLUT1).