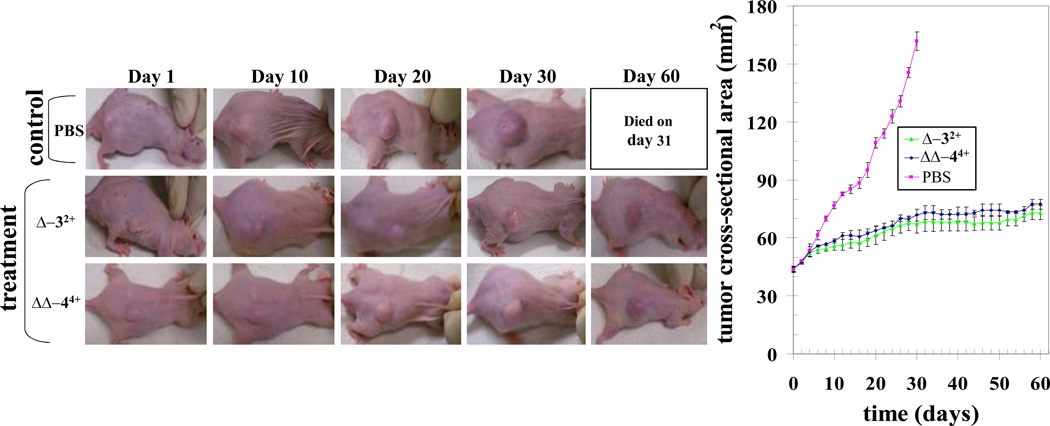
Fig. 4. Effect of ruthenium compounds on H358 human lung cancer nude mice xenograft model.
Hsd: Athymic nude nu/nu mice were obtained from Harlan, Indianapolis, IN. All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with a protocol approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Nine 10-week-old nude mice were divided into three groups of 3 animals (treated with PBS (pink), ruthenium compound Δ-3Cl2 (green) and ΔΔ-4Cl4 (blue) (70 mg / kg b.w.). All 9 animals were injected with 1 × 106 human lung cancer cells (H358) suspensions in 100 µl of PBS, subcutaneously into one flank of each nu/nu nude mouse. At the same time, animals were randomized treatment groups as indicated in the figure. Treatment was administered when the tumor surface area exceeded ~ 42 mm2 (day 24). Treatment consisted of Δ-32+ (2 mg) and ΔΔ-44+ (2 mg) in 200 µl PBS. Control groups were treated with 200 µl PBS. Animals were examined daily for signs of tumor growth. Tumors were measured in two dimensions using calipers. Photographs of animals were taken at day 1, day 10, day 20, day 30, and day 60 after treatment, are shown for all groups.