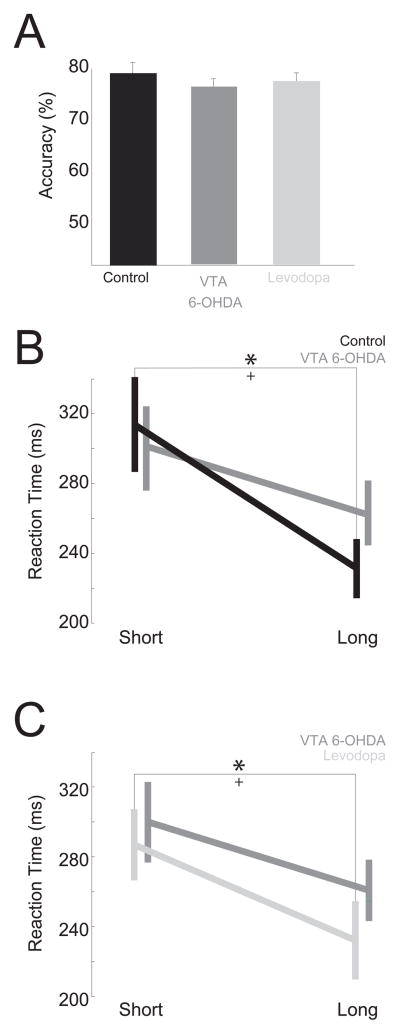
Figure 5.
VTA dopamine depletion attenuates temporal expectation in a simple reaction time task with two-delays. While VTA dopamine depletion did not change accuracy (A), control animals developed delay-dependent speeding and (B), animals with VTA dopamine depletion did not. They did nvvot learn delay-dependent speeding with further training. (C) Levodopa administration in VTA dopamine-depleted animals restored delay-dependent speeding. * indicates significant differences via a t-test at p<0.05; + indicates a significant interaction between dopamine depletion and delay-length in a linear random-effects model.