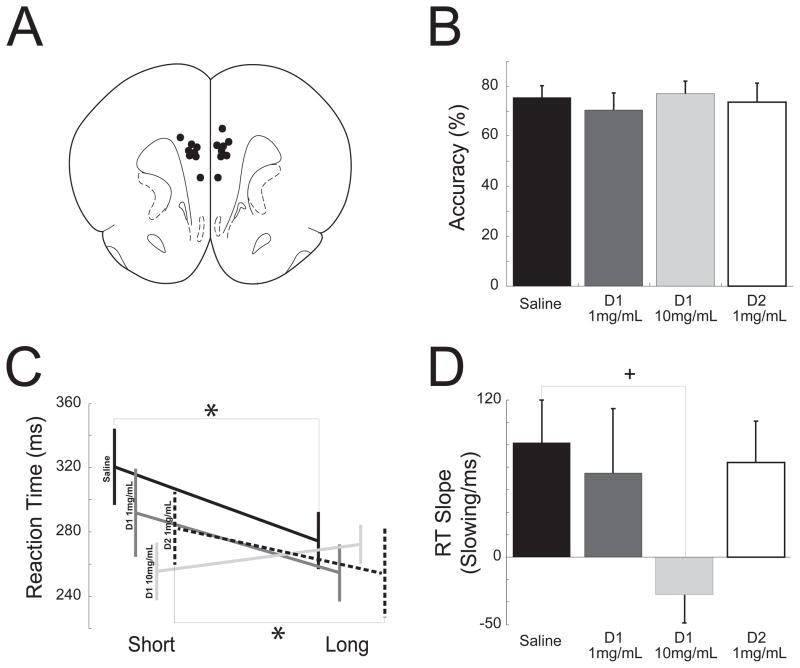
Figure 6.
Medial prefrontal D1 dopamine blockade attenuated temporal expectation. (A) Stereotaxic injections targeting the medial prefrontal cortex. Black dots (
 ) illustrate guide cannula locations. (B) There was no effect on accuracy following saline infusions, 1 mg/ml SCH23390 (D1 1 mg/ml), 10mg/ml SCH23390 (D1 10mg/ml), and 1 mg/ml sulpiride (D2 1 mg/ml) into the medial prefrontal cortex. (C) Following saline (black line) and sulpiride (dotted line), infusions to the medial prefrontal cortex, animals exhibited delay-dependent speeding as shown by faster reaction times (ms) during the long delay period (long) when compared to the short delay (short) in the simple reaction time task. However, following SCH23390 (D1; gray lines), animals had slower reaction times during the longer delays. (D) D1 blockade via SCH23390 attenuated the slope of delay-dependent slope while D2 blockade via sulpiride did not. * indicates significant differences via a t-test at p<0.05; + indicates a significant interaction between SCH23390 dose and delay-length in a linear random-effects model.
) illustrate guide cannula locations. (B) There was no effect on accuracy following saline infusions, 1 mg/ml SCH23390 (D1 1 mg/ml), 10mg/ml SCH23390 (D1 10mg/ml), and 1 mg/ml sulpiride (D2 1 mg/ml) into the medial prefrontal cortex. (C) Following saline (black line) and sulpiride (dotted line), infusions to the medial prefrontal cortex, animals exhibited delay-dependent speeding as shown by faster reaction times (ms) during the long delay period (long) when compared to the short delay (short) in the simple reaction time task. However, following SCH23390 (D1; gray lines), animals had slower reaction times during the longer delays. (D) D1 blockade via SCH23390 attenuated the slope of delay-dependent slope while D2 blockade via sulpiride did not. * indicates significant differences via a t-test at p<0.05; + indicates a significant interaction between SCH23390 dose and delay-length in a linear random-effects model.