Figure 5.
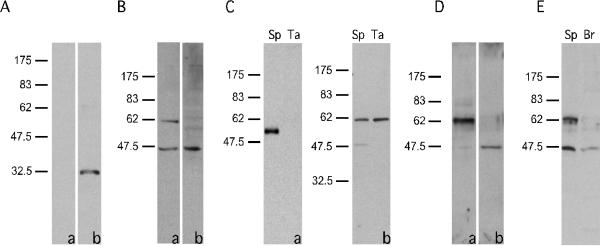
TEKT5 protein was present in sperm (Sp) and was particularly enriched in sperm flagellar accessory structures (Ta). (A): Preimmune serum (a) did not recognize the recombinant GST-TEKT5486-557 but immune serum (b) did. (B): Anti-GST-TEKT5486-557 recognized a ~62,000 Mr protein present in sperm, as well as a 43,000 Mr band (a). Reactivity of the ~62,000 Mr protein with the antibody was blocked by purified antigen GST-TEKT5486-557, while the 43,000 Mr signal was not, demonstrating the non-specific nature of this band (b). (C): The flagellar accessory structures lacked axonemal components as demonstrated by immunoblotting of equal amounts of sperm (Sp) and flagellar accessory structure protein (Ta). The axonemal protein, α–tubulin, was present in extracts of whole sperm but was absent in the flagellar accessory structure protein preparation (a). After 1% S-EDTA treatment, TEKT5 remained associated with the flagellar accessory structures, whereas the 43,000 Mr protein, which non-specifically bound to the anti-GST-TEKT5486-557 antibody, was solubilized. (b). (D): Equal amounts of protein from the 1% S-EDTA soluble supernatant or insoluble pellet (flagellar accessory structures) were analyzed by immunoblotting with the anti-GST-TEKT5486-557 antibody. This treatment effectively partitions the ~62,000 Mr protein into the S-EDTA insoluble fraction (a), whereas the non-specific 43,000 Mr signal was extracted into the supernatant (b). (E): The ~62,000 Mr, signal was detectable in sperm protein (Sp) but was absent in protein extracts of brain (Br).
